Bacteria
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A magnified image of several bacteria.
Bacteria are unicellular micro-organisms that have no nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplast but do have cytoplasm, a cell membrane and a cell wall.
About Bacteria
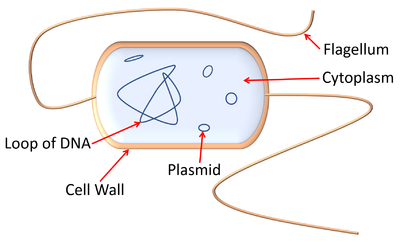
- Bacteria can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy.
- Some bacteria have a tail called a flagellum.
- Bacteria do not have a nucleus.
- The DNA of bacteria is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of DNA called plasmids.
| A diagram showing the features of a bacterium. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (with no membrane bound organelles) and are a domain of organisms in the three domain system.
About Bacteria
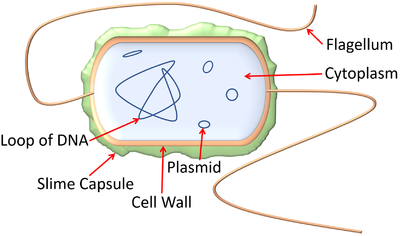
- Bacteria can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy.
- Disease causing bacteria are known as pathogenic bacteria.
- Some bacteria have a tail called a flagellum propel it move through water.
- Some bacteria are encased in a slime capsule which protects them from phagocytes and some toxic chemicals.
- Bacteria do not have a nucleus.
- The DNA of bacteria is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of DNA called plasmids.
| A diagram showing the features of a bacterium. |
References
AQA
- Bacteria (three-domain system), page 249, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria (three-domain system), page 309, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 11, 16, 17, 46, 48, 104, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 11, 42, 43, 80, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 124, 128, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 130, 134, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 2-4, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 3-4, 80, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria, pages 8-9, 76-83, 86-87, 100-103, 224, 230, 248-249, 252, 266, 269, 278, 282-283, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Bacteria, pages, 12, 22-3, 40-3, 97, 129, 138-9, 142-3, 282, 292-3, 300-1, 341, 346-7, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Bacteria; antibiotic resistance, page 89, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria; Antibiotic resistance, pages 61-3, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria; Binary fission, pages 28, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria; extremophile, 340-1, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Bacteria; Genetically engineered, pages 52, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Bacteria; identification of, page 83, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Bacterial cell, pages 22-3, 40-3, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Bacterial cells, page 24, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacterial cells, page 24, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacterial diseases, page 128, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacterial diseases, page 134, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Bacterial diseases, page 92, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Bacterial diseases, pages 79, 82-3, 103, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Bacteria (domain), page 137, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacteria, pages 10-11, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel'
- Bacteria, pages 10-11, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel'
- Bacteria, pages 11, 35, 39, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacteria, pages 12, 49, 55, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacteria, pages 24, 153-156, 301, 306, 307, 310, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacteria; cultures of, pages 63, 64, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacteria; genetic engineering, page 65, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel'
- Bacteria; genetic engineering, page 89, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel'
- Bacteria; nitrates, pages 142-143, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel'
- Bacteria; nitrates, pages 200-201, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel'
- Bacterial lawn plates, page 107, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel'
- Bacterial; cells, page 24, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel'
- Bacterial; cultures, pages 179-181, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel'
OCR
- Bacteria pages 12, 89, 91, 92, 97, 98, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Bacteria, pages 11, 67, 68, 73, 74, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Bacteria; antibiotics, pages 169, 228-229, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; cells, pages 20-21, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; colony isolation technique, page 231, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; decomposition, page 144, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; evolution, page 169, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; food poisoning, page 214, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; genetic engineering, pages 200, 202-203, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; identification, page 231, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; measurement, pages 262-263, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; plant disease, pages 216-217, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; transgenic bacteria, page 203, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Bacteria; zone of inhibition, pages 228-229, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR