Brain
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
The brain is an organ which can think and is found in the head of animals.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The brain is an organ in the nervous system which controls movement of the body.
Key Stage 4 Foundation
Meaning
The brain is part of the central nervous system which processes information sent by nerves.
About the Brain
- The brain is responsible for coordinating the muscles and glands around the body.
- The brain is the location of the pituitary gland which controls the release of hormones in the endocrine system.
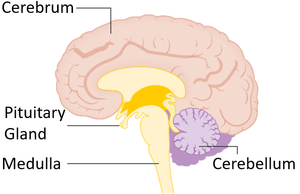
- There are several important structures in the brain including:
- The Cerebrum (or Cerebral Cortex) which deals with memory, language and conscious thought.
- The Cerebellum which deals with balance and the coordination of movement.
- The Medulla which controls the heartbeat, breathing and peristalsis in the digestive system.
- The Pituitary Gland which secretes hormones which control other endocrine glands in the body.
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
The brain is part of the central nervous system which processes information sent by nerves.
About the Brain
- The brain is responsible for coordinating the muscles and glands around the body.
- The brain is the location of the pituitary gland which controls the release of hormones in the endocrine system.
- There are several important structures in the brain including:
- The Cerebrum (or Cerebral Cortex) which deals with memory, language and conscious thought.
- The Cerebellum which deals with balance and the coordination of movement.
- The Medulla which controls the heartbeat, breathing and peristalsis in the digestive system.
- The Pituitary Gland which secretes hormones which control other endocrine glands in the body.
Investigating the Brain
- There are several ways in which the structure and function of different parts of the brain can be investigated.
MRI Scans
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a safe technique to observe the structure of a person's brain without surgery. It allows researchers to observe the size and shape of different structures in the brain and compare these to psychological traits of an individual.
- Recently an advance called fMRI has allowed researchers to observe the flow of blood in the brain which can indirectly show which parts of the brain are active when people think about different things. This has shown that thoughts, such as imagining a picture of a family member and performing a mathematical calculation, are done in separate areas of the brain.
Brain Damage
- It is not ethical to remove parts of people's brains just to see what happens. However, studying people who have had accidental brain damage allows us to get the same kind of information.
- People who have suffered from brain damage may should unusual behaviours. Researchers can relate these behavioural changes to which part of the brain is damaged, giving information about which parts of the brain are important in certain processes.
Direct Electrical Stimulation
- It is not ethical to open people's brains just to perform electrical stimulation to see what parts of the brain are involved in different processes. However, people who require brain surgery (for a variety of reasons) may consent to have this done for research purposes.
- Since neurons send electrical impulses around the brain it's possible to cause these by touching an electrode against the brain. Patients who have consented to this have demonstrated that stimulating parts of the brain may make them think of a song or a childhood memory.
References
AQA
- Brain, page 69, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Brain, pages 138-40, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Brain, pages 152-153, 160-161, 166-167, 170-171, 182-183, 187, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Brain, pages 171, 173, 178-9, 214, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Brain, pages 193, 194, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Brain problems, pages 40-41, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Brain tumours, page 41, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Brain, page 27, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Brain, page 34, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Brain, page 42, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Brain, pages 75, 76, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Brain, page 45, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Brain, pages 94-95, 97, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR