Key Stage 2
Meaning
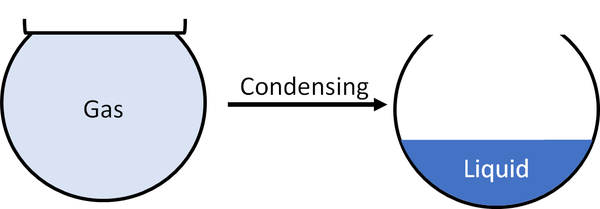
Condensing is when a gas turns into a liquid.
- Noun: Condensation
- Verb: To condense
- Present Participle: Condensing
When you cool a gas:
|
|
| A gas will condense to become a liquid.
|
About Condensing
- Cooling a gas will cause it to condense into a liquid.
- Condensing is a reversible process. When a gas condenses into a liquid you can evaporate that liquid back into a gas.
- You may have seen water condensing.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Condensing is an exothermic process in which a gas turns into a liquid.
About Condensing
- Condensing is a reversible process. When a gas condenses into a liquid you can evaporate that liquid back into a gas.
- Cooling a gas will cause it to condense into a liquid.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Condensing is an exothermic physical change in which a gas turns into a liquid.
About Condensing
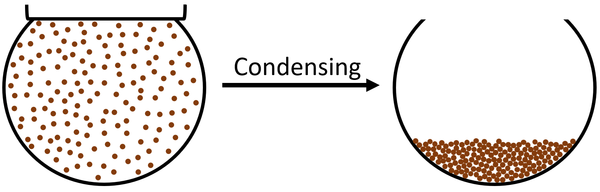
- Condensing happens when the particles in a gas form bonds holding them together as they lose potential energy.
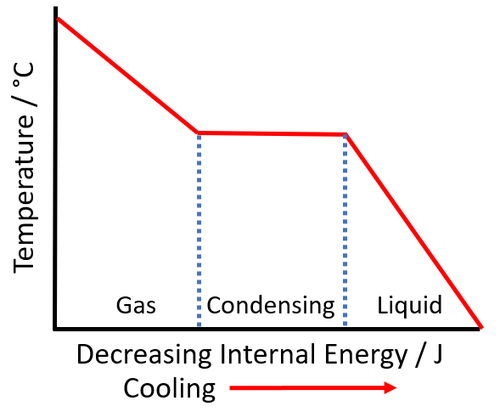
- The temperature at which a substance condenses is the same as the temperature at which it boils so it is the boiling point.
- Condensing is an exothermic process, which means it emits energy when it takes place.
- Condensing is a physical change, which means it is reversible and does not produce new chemicals.
References
AQA
- Condensing pages 39, 40, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, page 100, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, page 102, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, page 37, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, pages 100-102, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, pages 110-112, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Condensing, pages 68-9, 329, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Condensing, pages 89, 122, 195, 196, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Condesing, pages 88-9, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
OCR
- Condensing, pages 44, 82, 152, 154, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR