Boiling
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Boiling is when a liquid is so hot that all of it is turning into a gas.
About Boiling
Note to Teachers
The majority of students reaching secondary school do not know what the bubbles are made of when they observe water boiling. Answers to this question include; air, gas, hydrogen and oxygen. The more able students will generally state one of the latter two while few, if any, will state that it is water vapour or water gas. It appears that while students tacitly accept that boiling means liquid turning into gas, they don't fully understand the implications.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Boiling is an endothermic process in which a substance turns from a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
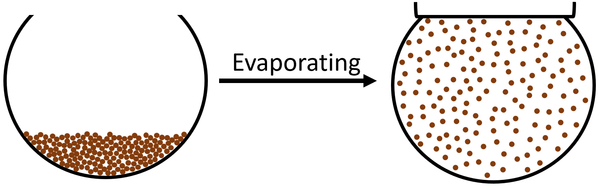
About Evaporating
- Boiling is a reversible process. When a liquid boils and becomes a gas you can condense that gas back into a liquid.
- A liquid will boil when it has been heated to its boiling point.
| The particles in the liquid move faster until they are moving fast enough that they break the bonds holding the particles together. The particles become free to move anywhere which makes the state a gas. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Boiling is an endothermic physical change in which a substance turns from a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
About Boiling
- Boiling is different from evaporating because:
- During evaporation only particles on the surface can escape the liquid to form part of a gas. Whereas when a liquid is boiling all of the particles have enough energy to spread apart to make a gas.
- Boiling happens at the boiling point. Whereas evaporation can happen at temperatures below the boiling point of the liquid.
- Boiling happens when the particles in a liquid have enough energy to break bonds holding them close to one another as they gain potential energy.
- The temperature at which a substance boils is called its boiling point.
- Boiling is an endothermic process, which means it needs to absorb energy to take place.
- Boiling is a physical change, which means it is reversible and does not produce new chemicals.
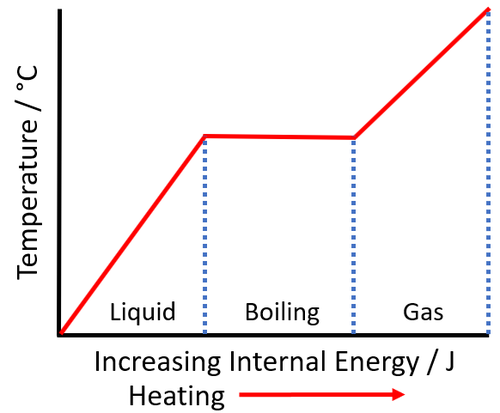
| As a liquid is heated the internal energy increases. As the liquid boils the temperature of the substance stays the same but the potential energy of the particles continues to increase. |
References
AQA
- Boiling, page 100, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, page 102, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, page 122, 195, 196, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, page 324, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Boiling, page 37, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, page 72, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Boiling, pages 100, 101, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, pages 110, 111, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, pages 39, 40, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Boiling, pages 88-9, 94-5, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA