Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
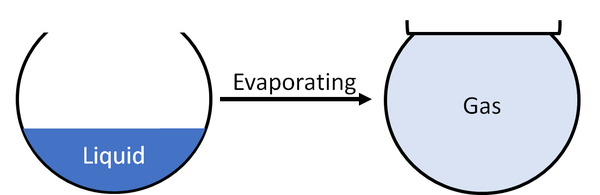
Evaporating is when a liquid turns into a gas.
- Noun: Evaporation
- Verb: To evaporate
- Present Participle: Evaporating
| A liquid will evaporate to become a gas. |
About Evaporating
- Heating a liquid will cause it to evaporate into a gas.
- Evaporation is a reversible process. When a liquid evaporates into a gas you can condense that gas back into a liquid.
- You may have seen these evaporating:
- Water
- Hand Gel
Examples
| When water is boiling the liquid evaporates turning into a gas. Eventually all the liquid will be gone and the room will be filled with water vapour. | When you use Hand Gel the liquid quickly evaporates from your hands so you don't need to dry them. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Evaporating is an endothermic process in which a liquid turns into a gas.
About Evaporating
- Evaporation is a reversible process. When a liquid evaporates into a gas you can condense that gas back into a liquid.
- Heating a liquid will cause it to evaporate more quickly into a gas.
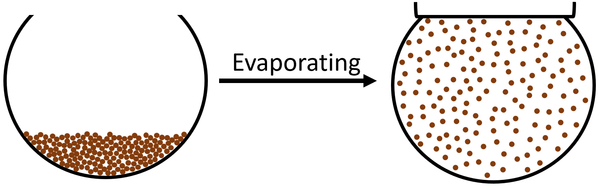
| The particles in the liquid move faster until they are moving fast enough that they break the bonds holding the particles together. The particles become free to move anywhere which makes the state a gas. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Evaporating is an endothermic physical change in which the particles on the surface of a liquid are able to escape the liquid to become part of a gas.
About Evaporating
- Evaporating is different from boiling because:
- Evaporation happens from the surface of the liquid.
- Evaporation can happen at temperatures below the boiling point of the liquid.
- Evaporating happens when some particles at the surface of a liquid have enough energy to escape the bonds holding the particles together in the liquid.
- Evaporation is an endothermic process, which means it needs to absorb energy to take place. When liquids evaporate the temperature of the liquid decreases as the energy is taken away by the particles escaping the liquid.
- Evaporating is a physical change, which means it is reversible and does not produce new chemicals.
References
AQA
- Evaporation, page 100, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 112, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 23, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Evaporation, page 269, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 330, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 38, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 38, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, page 72 GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Evaporation, page 81, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Evaporation, pages 17, 37, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Evaporation, pages 66-69, 272-273, 279, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Evaporation, pages 9-10, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Evaporation, pages 97, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Evaporation, pages, 137, 138, 324, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Evaporation, pages, 69, 114, 329, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Evaporations, page 110, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Evaporations, pages 39, 40, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Evaporation, page 35, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Evaporation, page 98, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Evaporation, pages 10, 152, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Evaporation, pages 154, 266, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel