Key Stage 3
Meaning
The gas exchange system in plants allows them to absorb and release both Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide.
About Gas Exchange in Plants
- Unlike animals plants do both respiration and photosynthesis. This means sometimes they take in more Oxygen and release more Carbon Dioxide and other times they take in more Carbon Dioxide and release more Oxygen. Overall a plant makes more Oxygen than Carbon Dioxide.
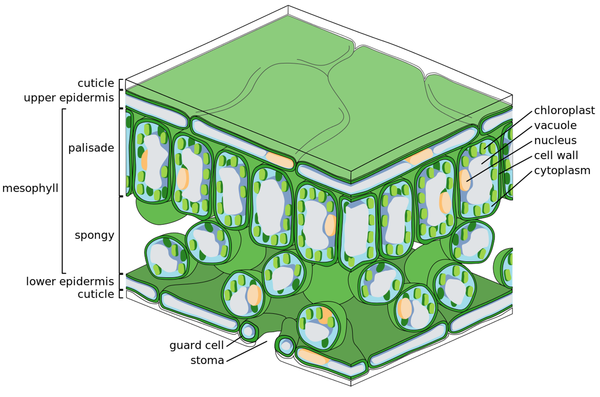
Gas Exchange in the Leaf
- Leaves have air gaps between the spongy mesophyll cells to allow gas exchange.
- Leaves usually have more guard cells and stomata on the underside (lower epidermis) than the top side (upper epidermis). These close when the leaf gets dehydrated, stopping carbon dioxide getting into the leaf which stops them using water for photosynthesis.
Edexcel
- Gas exchange; plants, pages 211-214, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Gas exchange; plants, pages 72, 73, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel