Reflex Arc
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The reflex arc is the path taken by an electrical impulse to cause an automatic reflex reaction.
About the Reflex Arc
- Sometimes a change in the environment is so dangerous it would cause more damage to have to think about it before reacting to it. This is the case for very high temperatures. If the skin begins to burn this will cause more damage the longer it takes to react. Animals have evolved reflex reactions to react quickly to prevent unnecessary damage.
- Reflex reactions take place when an impulse is sent along the reflex arc.
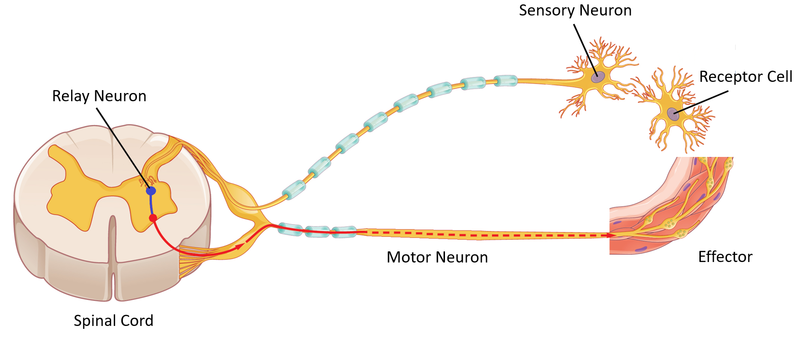
- The impulse in the reflex arc does not pass to the brain to be processed. It is sent to the spinal cord then to an effector. This provides a shorter path for the impulse so results in a shorter reaction time.
The reflex arc can be described in several stages:
- Stimulus - A change to the external environment.
- Receptor Cell - A specialised cell detects the change in the environment and produces an electrical impulse.
- Sensory Neuron - The impulse is transmitted to the spinal cord.
- Relay Neuron - The impulse is relayed from the sensory neuron to a motor neuron.
- Motor Neuron - The impulse is transmitted from the spinal cord to an effector.
- Effector - A muscle receives the impulse form the motor neuron.
- Reaction - The muscle contracts causing part of the body to move uncontrollably.
| A diagram showing the reflex arc. |
References
Edexcel
- Reflex arc, page 47, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Reflex arcs, page 73, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel