Sampling (Biology)
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Sampling is when a scientist looks at several small areas of an organism or an ecosystem and calculates a mean average to make an estimate over the total area.
About Sampling
- Sampling is used when it is not possible to count all of a specific feature within an entire organism or ecosystem.
- Sampling allows a scientist to estimate the total spread of a feature over an entire organism or ecosystem.
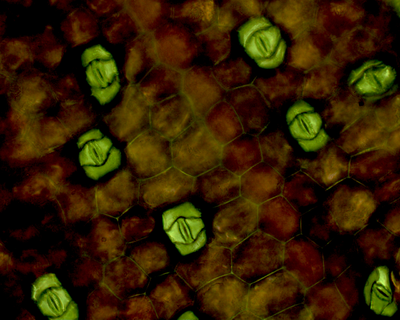
- When sampling the features of an organism a microscope may be used to several small sections of that organism.
- When sampling small plants in an ecosystem a quadrat may be used to find the number of those plants in a given area.
Examples
| The number of stomata in the sample is counted and the number of stomata on the leaf can be estimated by multiplying the number in this area by the number of these areas that would fit on a leaf. | The fraction of plant coverage within the quadrat sample is counted by adding up the number of squares with plant coverage then this area. The same is done for several other areas within this ecosystem and a mean average is taken to estimate the average coverage of plants within this ecosystem. |
References
AQA
- Sampling, pages 251-5, 267-8, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Sampling, pages 293, 294, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Sampling, pages 328-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Sampling, pages 373, 374, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Sampling, pages 5, 240, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Sampling, pages 67, 262-263, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Sampling, pages 89-100, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Sampling; Using quadrats, pages 90-3, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA