Solenoid
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A solenoid is a coil of wire which produces a magnetic field, similar to that of a bar magnet, when it has an electrical current.
About Solenoids
- Solenoids can be used to magnetise a magnetic material.
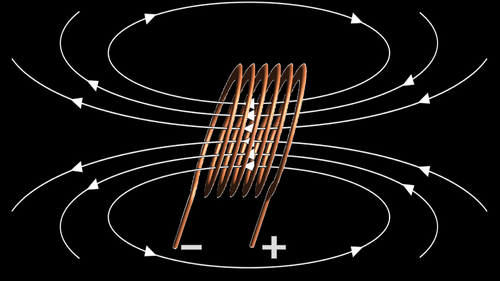
- Solenoids have a uniform magnetic field inside the coil of wire and a non-uniform magnetic field outside the coil, similar to that of a bar magnet.
- The magnetic field is strongest inside the coil.
- Solenoids are not magnets themselves, but they are part of an electromagnet. To turn a solenoid into an electromagnet it needs a soft iron core.
- The strength of a solenoid depends upon:
- The current in the coil - The greater the current the stronger the magnetic field.
- The number of coils - The greater the number of coils the stronger the magnetic field.
| This diagram shows the magnetic field lines of a solenoid. The inside of the solenoid has a uniform magnetic field. |
References
AQA
- Solenoid, pages 248, 252, 258-9, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Solenoid; production of a magnetic field, page 225, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Solenoids, page 230, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Solenoids, page 93, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Solenoids, pages 217-219, 223, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Solenoids, pages 218, 219, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Solenoids, pages 279, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Solenoids, pages 291, 292, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Solenoids; in relays, page 226, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Solenoids; induced current, page 233, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Solenoids, page 171, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Solenoids, page 198, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Solenoids, page 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Solenoids, pages 270, 271, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel