Wire
Contents
Key Stage 1
Meaning
Wires are long pieces of metal covered in plastic.
About Wires
- Wires carry electricity which can hurt you.
- You should not touch a wire unless an adult says it is safe.
- If the plastic has come off a wire and you can see the metal you should tell an adult as soon as you can.
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A wire is a long piece of metal used to carry electricity. It is usually covered in plastic to prevent electrical shocks.
About Wires
- Wires are used to connect electrical components together.
- Electricity flows through the metal in the wires.
- A wire is usually covered in plastic for safety. The plastic is safe to touch, but if you can see the metal then it is dangerous and could electrocute you if you touched it.
- Wires come in many sizes. The thicker the wire the more electricity it carries and the more dangerous it is.
- The metal inside a wire is an electrical conductor which means electricity can pass through it easily.
- The plastic covering the wire is an electrical insulator which means electricity does not pass through it very easily.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A wire is a long, thin piece of metal that allows electricity through it.
About Wires
- Wires are used to connect electrical components together.
- Electrons flow through the metal in the wires as an electrical current.
- A wire is usually covered in an insulator such as plastic. This prevents electrical current leaving the wire when it is touched by an electrical conductor. This also prevents electrocution.
- The metal inside a wire is an electrical conductor which means electricity can pass through it easily.
- The plastic covering the wire is an electrical insulator which means electricity does not pass through it very easily.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A wire is a long, thin piece of metal that allows electricity through it.
About Wires
- Wires are used to connect electrical components together.
- Electrons flow through the metal in the wires as an electrical current.
- A wire is usually covered in an insulator such as plastic. This prevents electrical current leaving the circuit when the wires are touched. This also prevents electrocution.
- Wires are heated by an electrical current passing through them.
- Wires are designed to be a low resistance in order to allow an electrical current through them without losing too much energy by heating the wires.
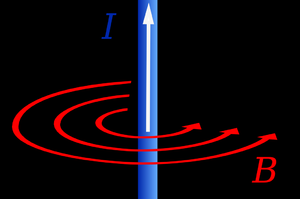
Magnetic Field of a Wire
- When there is a current in a wire the wire has a magnetic field which acts around that wire.
| The magnetic field of a current carrying wire. | |
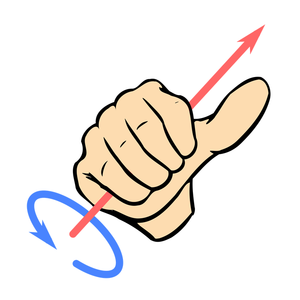
| The direction of the magnetic field can be shown by the 'right hand thumb rule' with thumb pointing in the direction of the current the fingers will wrap around in the direction of the magnetic field. |
The strength of the magnetic field of a wire depends on:
- The current in the wire - The greater the current the stronger the magnetic field.
- The distance from the wire - The greater the distance from the wire the weaker the magnetic field.
References
AQA
OCR
- Wires; Characteristic graph for, page 106, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Wires; Electrons, pages 105, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Wires; Forces on, page 126-127, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Wires; Magnetic fields, pages 122-123, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Wires; Spinning coils, pages 122-123, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR