Electron
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
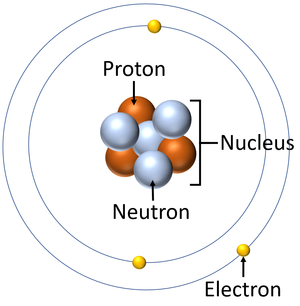
An electron is a small particle found orbiting the centre of an atom.
About Electrons
- Electrons negatively charged.
- In conductors electrons can pass easily from one atom to the next.
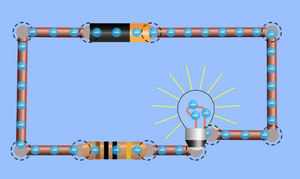
- When electrons move it is called an electrical current.
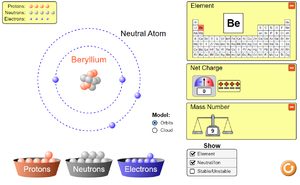
To see how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of atoms or to see how electrons move around a circuit click on the pictures below to play a PHET simulation.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Electron is a negatively charged particle found orbit the nucleus of an atom in electron shells.
About Electrons
- Electrons have a relative atomic charge of -1 and a relative atomic mass of 1/1840.
- The electrons and their shells are responsible for the chemistry of an atom.
- When atoms bond to form molecules some atoms can share their electrons forming a Covalent Bond, some transfer an electron from one atom to another forming an Ionic Bond while others allow electrons to pass freely between many atoms forming a Metallic Bond.
Key Stage 5
Meaning
An electron (e) is a type of lepton with a mass of 9.11x10-31kg and charge of -1.60x10-19 Coulombs.
About Electrons
- The electron is denoted with a lower case e.
- Electrons are fundamental particles as they are not made of any smaller particles.
- Electrons are affected by the:
| Lepton | Charge/e | Strangeness | Baryon Number | Lepton Number |
| \(Q=-1\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=0\) | \(L=+1\) | |
| \(Q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=0\) | \(L=+1\) | |
| \(Q=+1\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=0\) | \(L=-1\) | |
| \(Q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=0\) | \(L=-1\) |
References
AQA
- Electron, pages 12-3, 22, 24-5, 106, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Electron; delocalisation, pages 37, 56, 59, 66-7, 82-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Electron; sharing, pages 38-9, 58, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Electron; shell, pages 22-3, 30-1, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Electron; transfer, pages 37-9, 58, 60-1, 164-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Electrons, page 5, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons, page 88, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons, pages 110, 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 117-18, 338, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons, pages 12, 19, 20, 23, 28-32, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 122-124, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 22, 23, 25, 42-45 72-76, 80-85, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 22, 23, 25, 42-45, 70-74, 78-83, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 2-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons, pages 35, 43-45, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Electrons, pages 50-55, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons, pages 96, 104, 105, 113, 114, 116, 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; beta particles, page 115, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; beta particles, page 127, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; charge, page 14, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; chemical cells, pages 120-121, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; delocalised, page 45, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons; delocalised, pages 49-51, 53, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; discovery of, page 341, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons; discovery of, page 91, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons; discovery, page 108, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; discovery, page 120, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; discovery, pages 12-13, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; electrolysis, pages 104-105, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; in oxidation and reduction reactions, page 103, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons; in oxidation and reduction reactions, pages 204-5, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Electrons; ions, pages 16, 38-43, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; metallic bonding, page 53, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; movement of, page 61, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; movement of, pages 63, 99, 100, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; periodicity, pages 19, 24-25, 30-31, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Electrons; shells, pages 12, 19, 20, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; shells, pages 22, 43-45, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; shells, pages 22, 43-45, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; shells, pages 96, 104, 105, 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Electrons; shielding, pages 30-31, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Electrons, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 151, 152, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 16, 19, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 162, 354, 380, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 32-36, 42, 43, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 49, 50, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 79, 82, 172, 173, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons, pages 90, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Electrons; annihilation, pages 157, 170, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons; beta particles, pages 156, 157, 159, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons; in atoms, pages 151, 152, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Electrons; movement between energy levels, pages 128, 153, 154, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Electrons, pages 14, 17, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Electrons, pages 18, 21, 94, 96-97, 105, 170, 178-179, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons, pages 27, 29, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons, pages 86-86, 88-90, 92, 150, 175, 195, 196, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Electrons; covalent bonds, page 60, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons; energy levels, pages 84, 88, 196, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Electrons; free elections, pages 94, 96, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Electrons; ionic bonds, page 58, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons; metallic bonds, pages 66-67, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons; periodic table, pages 70-71, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Electrons; redox reactions, page 111, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
An electron is a subatomic particle with a negative charge and a very small mass.
About Electrons
- Electrons are fundamental particles classified as leptons.
- The rest mass of an electron is 9.11×10−31kg.
- An electron has an electrical charge of −1.60×10−19 Coulombs.
- Electrons participate in chemical bonding and electricity.
- Electrons can be emitted from a metal surface through the photoelectric effect when exposed to electromagnetic radiation of sufficient frequency.
- Electrons move around the nucleus of an atom in discrete energy levels or shells.
- Electrons can move between energy levels in atoms by absorbing the exact energy required from an incident photon or from the kinetic energy of another electron colliding with it.
- The [antimatter]] counterpart of the electron is the positron.