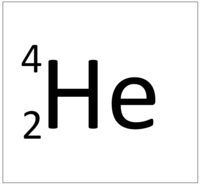Relative Atomic Mass
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An element tile showing the mass number.
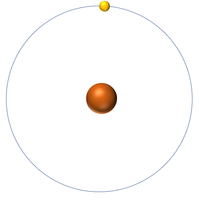
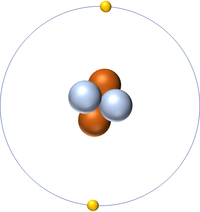
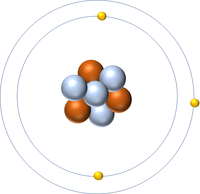
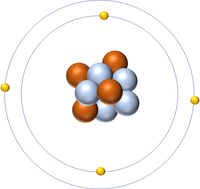
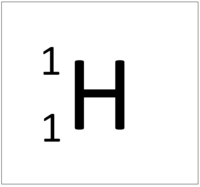
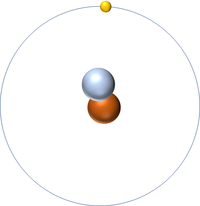
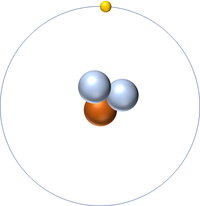
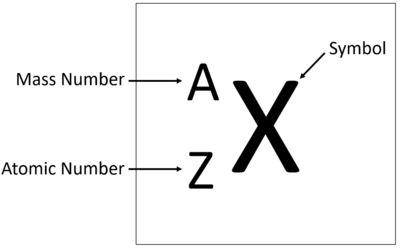
The Atomic Mass or mass number is the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom.
About The Atomic Mass
- Two atoms of the same element may have the same Atomic Number but a different Atomic Mass depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Elements with different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- The atomic mass is not affected by the number of electrons.
- Only the particles in the nucleus affect the atomic mass.
Examples
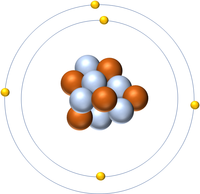
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| Hydrogen has one nucleon so it has an atomic mass of 1. | Helium has four nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 4. | Lithium has seven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 7. | Beryllium has nine nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 9. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning

An element tile showing the mass number.
The relative atomic mass or mass number of an element is the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons) in an atom.
The relative atomic mass in grams is also the mass of one mole or 6.02x1023 atoms of the element.
About Relative Atomic Mass
- The relative atomic mass in grams on the Periodic Table tells the mass of a mole of the element. A mole of the element is 6.02x1023 atoms of that element.
- Two atoms of the same element may have the same Atomic Number but a different Relative Atomic Mass depending on the number of neutrons in the nucleus. Elements with different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- The relative atomic mass is not affected by the number of electrons.
- Only the particles in the nucleus affect the relative atomic mass.
Examples
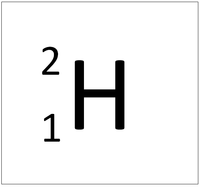
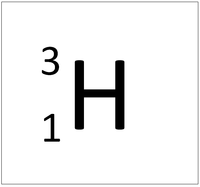
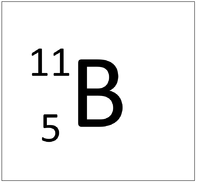
| Hydrogen | Deuterium | Tritium | Boron |
| Hydrogen has one nucleon so it has an atomic mass of 1 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Hydrogen have a mass of 1g. | Deuterium has two nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 2 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Deuterium have a mass of 2g. | Tritium has three nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 3 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Tritium have a mass of 3g. | Boron has eleven nucleons so it has an atomic mass of 11 and 6.02x1023 (or 1 mole of) atoms of Boron have a mass of 11g. |
References
AQA
- Relative atomic mass (Ar), pages 4-5, 64, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, A, pages 13, 21, 41, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, A, pages 97, 123, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 100-1, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 120, 177, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 106, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 26, 112, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Relative atomic mass, pages 62-63, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Ar (relative atomic mass), page 167, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Ar (relative atomic mass), page 23, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Relative atomic masses (RAM), pages 23, 26, 29, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Relative atomic masses, pages 17, 28, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Relative atomic masses, pages 37, 38, 85, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Relative atomic masses, pages 80, 91, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel