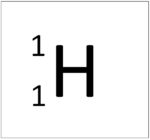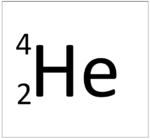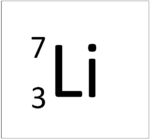Neutron
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The Neutron is a neutral particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
About Neutrons
- Neutrons are a type of nucleon.
- Neutrons have a relative atomic charge of 0 and a relative atomic mass of 1.
- The number of neutrons in an atom can be found subtracting the Atomic Number from the Relative Atomic Mass.
| Hydrogen | Helium | Lithium | Beryllium |
| This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 1 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 1.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 1 - 1 Number of neutrons = 0 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 2 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 4.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 4 - 2 Number of neutrons = 2 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 3 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 7.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 7 - 3 Number of neutrons = 4 |
This atom has an Atomic Number (Z) of 4 and a Relative Atomic Mass (A) of 9.
Number of neutrons = A - Z Number of neutrons = 9 - 4 Number of neutrons = 5 |
References
AQA
- Neutron, pages 108-11, 130, 133, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Neutron, pages 13, 24-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Neutron; radiation, pages 112, 128, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Neutrons, page 2-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Neutrons, page 88, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 110, 111, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 117-18, 338, 339, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 12, 13, 19, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 122, 123, 140, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 13-17, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 22-25, 43, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 22-25, 43, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 43-45, 49, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Neutrons, pages 96, 97, 104, 197, 198, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Neutrons, page 16, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Neutrons, page 79, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons, pages 152, 155, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons, pages 162, 356, 380, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Neutrons, pages 33-37, 48, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons, pages 92, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Neutrons; in fission reactions, pages 173, 174, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons; nuclear decays, page 157, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Neutrons; nuclear equations, page 160, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Neutrons, pages 20-21, 170-172, 179,184, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR
- Neutrons, pages 27, 28-29, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Neutrons, pages 84-86, 150, 195, 197, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
A neutron (n) is a baryon made from 1 up-quark and 2 down-quarks.
About Neutrons
- The neutron is denoted with a lower case n.
- A neutron is one of two baryons found in the atomic nucleus.
- Neutrons have a charge of zero and a mass of 1.67x10-27kg.
- A neutron is only stable in the nucleus of an atom. However a free neutron has a mean lifeftime of around 15 minutes before it decays via the weak interaction into a proton and an electron.
| Subatomic Particle | Quark-composition | Charge/e | Strangeness | Baryon Number | Lepton Number |
| \(udd\) | \(Q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=+1\) | \(L=0\) | |
| \(\bar{u}\bar{d}\bar{d}\) | \(Q=0\) | \(S=0\) | \(B=-1\) | \(L=0\) |