Energy Level
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Energy Levels are another name for the electron shells or orbitals around the nucleus where electrons can exist.
About Energy Levels
- The existence of energy levels in atoms is part of the Bohr model of the atom.
- The electron orbitals in atoms each correspond to electrons with a certain amount of energy, which is why they are also called energy levels.
- Electrons cannot exist anywhere between the energy levels they can only exist in one energy level or another.
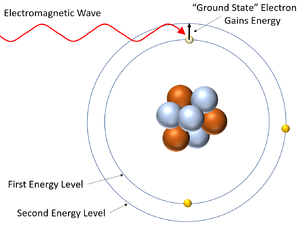
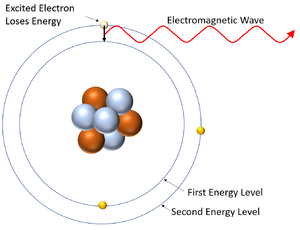
- In chemistry electrons are seen as fixed in their energy levels but in physics the electrons can move to a higher energy level by the absorption of energy and can drop down into an empty energy level below by emitting energy.
- The wavelengths of electromagnetic wave depend on the energy difference between the energy levels in atoms.
| This diagram shows an electron gaining energy by absorbing an electromagnetic wave and moving to a higher energy level (becoming excited). | This diagram shows an excited electron losing energy by emitting an electromagnetic wave. As it does this the electron falls back down to a lower energy level. |
- If an electron in an the highest energy level, known as the outer shell, gains enough energy it can leave the atom completely so they atom becomes a positive ion.
References
AQA
- Energy level of electrons, pages 13, 18-19, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Energy levels (atoms), page 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Energy levels (electron shells), pages 22, 43-45, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Energy levels (electron shells), pages 22, 43-45, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Energy levels (shells), page 117-18, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Energy levels (shells), pages 2,3,5, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Energy levels in atoms, page 43, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Energy levels in atoms, pages 111, 201, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Energy levels in atoms, pages 123, 243, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Energy level diagrams, pages 155, 156, 167, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Energy level diagrams, pages 180, 181, 199, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Energy levels in atoms, pages 128, 151, 153, 154, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Energy levels, pages 49, 50, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Energy levels are the discrete amounts of energy that electrons in an atom can have.
About Energy Levels
- Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
- When an electron absorbs energy, it can move to a higher energy level (excitation in which the atom is said to be excited. NB: not the electron itself).
- When an electron falls to a lower energy level, it emits energy in the form of a photon.
- The energy difference between levels determines the frequency of the emitted or absorbed photon.
- Energy levels are quantized, meaning electrons can only exist in these specific levels and not in between.
- The transitions between energy levels are responsible for the absorption and emission spectra of atoms.