Difference between revisions of "Direct Current"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC1.png|center| | + | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC1.png|center|290px]] |
| − | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC2.png|center| | + | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC2.png|center|290px]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
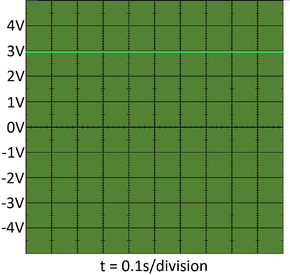
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:290px; text-align:center;" |This is a constant '''direct current''' from a 3V [[battery]]. |
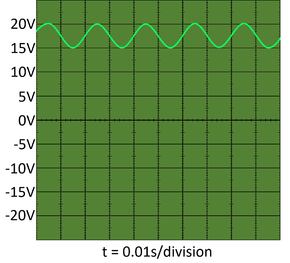
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:290px; text-align:center;" |This is a fluctuating '''direct current'''. |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | |- |
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC3.png|center|290px]] |
| + | |[[File:OscilloscopeScreenDC4.png|center|290px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
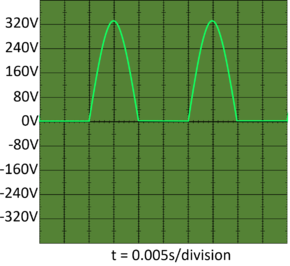
| + | | style="height:20px; width:290px; text-align:center;" |This is the '''direct current''' caused by [[Mains Electricity|mains electricity]] being passed through a [[diode]]. | ||
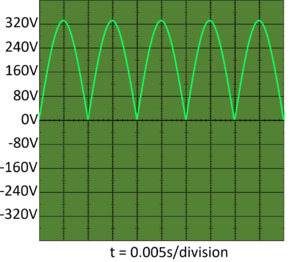
| + | | style="height:20px; width:290px; text-align:center;" |This is the '''direct current''' caused by [[Mains Electricity|mains electricity]] being passed through a [[Rectifier]] which is a set of [[diode]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 1 March 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Direct current (DC)is when electricity only flows in one direction.
About Direct Current
- Direct current is produced by electrical cells, batteries and dynamos.
- Direct current can be made from an alternating current using a diode.
- Direct current is needed to charge a cell or battery.
- Direct current is used in electrolysis.
Examples
| This is a constant direct current from a 3V battery. | This is a fluctuating direct current. |
| This is the direct current caused by mains electricity being passed through a diode. | This is the direct current caused by mains electricity being passed through a Rectifier which is a set of diode. |