Difference between revisions of "Star"
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===About Stars=== | ===About Stars=== | ||
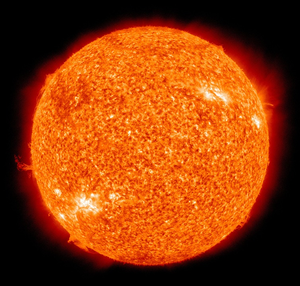
: [[The Sun]] is the closest [[star]] to [[Earth]]. | : [[The Sun]] is the closest [[star]] to [[Earth]]. | ||
| − | : [[Star]]s come in many different sizes. Our [[The Sun|Sun]] is a medium | + | : [[Star]]s come in many different sizes. Our [[The Sun|Sun]] is a medium sized [[star]] called a [[Main Sequence Star]]. |
: Most [[star]]s in the [[Universe]] are smaller than [[The Sun]] and are often [[White Dwarf]]s. However, there are many [[star]]s that are much larger than [[The Sun]] and are often [[Red Giant]]s or [[Red Supergiant]]s. | : Most [[star]]s in the [[Universe]] are smaller than [[The Sun]] and are often [[White Dwarf]]s. However, there are many [[star]]s that are much larger than [[The Sun]] and are often [[Red Giant]]s or [[Red Supergiant]]s. | ||
: [[Star]]s are held together in large groups called a [[Galaxy]]. | : [[Star]]s are held together in large groups called a [[Galaxy]]. | ||
Revision as of 21:52, 25 March 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A star is a very large ball of gas in space that is glowing in visible light because it is so hot.
About Stars
- The Sun is the closest star to Earth.
- Stars come in many different sizes. Our Sun is a medium sized star called a Main Sequence Star.
- Most stars in the Universe are smaller than The Sun and are often White Dwarfs. However, there are many stars that are much larger than The Sun and are often Red Giants or Red Supergiants.
- Stars are held together in large groups called a Galaxy.
- The Sun is the only star close enough to affect the Earth. Most stars are many light years away.
- The closest star to The Sun is Alpha Centauri which is 4.23 Light Years away.
| This image shows thousands of stars. |