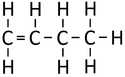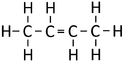Difference between revisions of "Butene"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== Butene is a gaseous (at room temperature) hydrocarbon with chemical formula C<sub>3</sub>H<...") |
(→About Butene) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
===About Butene=== | ===About Butene=== | ||
| + | : There is more than one [[isomer]] of [[Butene]]. | ||
====Bute-1-ene==== | ====Bute-1-ene==== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 10:48, 3 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Butene is a gaseous (at room temperature) hydrocarbon with chemical formula C3H6.
About Butene
- Butene is hydrocarbon because it contains only Hydrogen and Carbon atoms.
- Butene can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butene + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Butene is a gaseous (STP) hydrocarbon with chemical formula C3H6.
About Butene
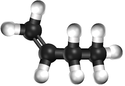
Bute-1-ene
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n) | Structural Formula | Structural Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| C4H8 | CH2CHCH2CH3 |
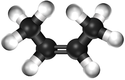
Bute-2-ene
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n) | Structural Formula | Structural Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| C4H8 | CH3CHCHCH3 |
- Butene is hydrocarbon because it contains only Hydrogen and Carbon atoms.
- Butene has a double bond between two Carbon atoms.
- Butene is described as 'unsaturated' due to the double bond as it is not completely 'saturated' by Hydrogen atoms like Butane.
- Butene can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butene + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C3H6 + 9O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O</chem>