Difference between revisions of "Ultrasound Imaging"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: [[Ultrasound]] can be [[reflect]]ed, [[refracted]] or [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] at the [[interface]] between different [[media]]. This can be used, along with a computer, to create images of the internal structure of an [[object]]. This is particularly useful for [[opaque]] [[object]]. | : [[Ultrasound]] can be [[reflect]]ed, [[refracted]] or [[Absorb (Physics)|absorbed]] at the [[interface]] between different [[media]]. This can be used, along with a computer, to create images of the internal structure of an [[object]]. This is particularly useful for [[opaque]] [[object]]. | ||
: [[Ultrasound]] is generally used to detect cracks in large [[metal]] structures using [[echolocation]]. | : [[Ultrasound]] is generally used to detect cracks in large [[metal]] structures using [[echolocation]]. | ||
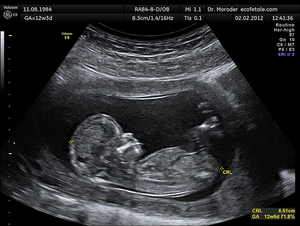
| − | : [[Ultrasound]] is used in hospitals to create images of [[organ]]s and of the [[foetus]] of [[pregnant]] [[female]]. | + | : [[Ultrasound]] is used in hospitals to create images of [[organ]]s and of the [[foetus]] of [[pregnant]] [[female]]s. |
Latest revision as of 11:44, 5 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Ultrasound imaging is a technique that uses ultrasound to form an image of the internal structure of an object.
About Ultrasound Imaging
- Ultrasound can be reflected, refracted or absorbed at the interface between different media. This can be used, along with a computer, to create images of the internal structure of an object. This is particularly useful for opaque object.
- Ultrasound is generally used to detect cracks in large metal structures using echolocation.
- Ultrasound is used in hospitals to create images of organs and of the foetus of pregnant females.