Difference between revisions of "Gravitational Field Strength"
(→Meaning) |
(→Meaning) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | '''Gravitational Field Strength''' is the [[force]] | + | '''Gravitational Field Strength''' is the [[force]] per [[kilogram]] on an [[object]] in a [[Gravitational Field|gravitational field]]. |
===About Gravitational Field Strength=== | ===About Gravitational Field Strength=== | ||
Revision as of 20:00, 21 August 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gravitational Field Strength is the force per kilogram on an object in a gravitational field.
About Gravitational Field Strength
- On Earth gravitational field strength is roughly 10 Newtons for each kilogram of mass (10N/kg).
- Different objects have different gravitational field strengths.
Examples
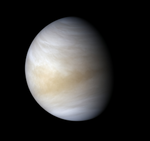
| Mercury | Venus | Earth |
| 4N/kg | 9N/kg | 10N/kg |
| The Moon | Mars | Jupiter |
| 4N/kg | 20N/kg | 10N/kg |
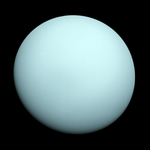
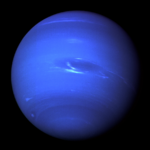
| Saturn | Uranus | Neptune |
| 9N/kg | 10N/kg | 2N/kg |
| The Sun | ||
| 300N/kg |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Gravitational Field Strength is the force per kilogram on an object in a gravitational field.
About Gravitational Field Strength
- At sea level on Earth the gravitational field strength is 9.8 Newtons for each kilogram of mass (9.8N/kg).
Gravitational Field Strength depends on:
- The mass of the moon, planet or star - The larger the mass the greater the gravitational field strength.
- Distance from the centre of mass of the moon, planet or star - The larger the distance the smaller the gravitational field strength.
| Mercury | Venus | Earth |
| 3.7N/kg | 8.8N/kg | 9.8N/kg |
| The Moon | Mars | Jupiter |
| 1.7N/kg | 3.7N/kg | 24N/kg |
| Saturn | Uranus | Neptune |
| 11N/kg | 9.0N/kg | 12N/kg |
| The Sun | ||
| 290N/kg |