Difference between revisions of "Concave Lens"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
The [[diagram]] shows that a [[diminish]]ed [[Virtual Image|virtual image]] is produced at the point that the 'traced' lines from "ray 1" and "ray 2" cross one another. | The [[diagram]] shows that a [[diminish]]ed [[Virtual Image|virtual image]] is produced at the point that the 'traced' lines from "ray 1" and "ray 2" cross one another. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Concave lenses, page 206, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Concave lenses, page 71, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Concave lenses, pages 208-211, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Concave lenses, pages 267, 268, 273, 274, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac60 ''Concave lenses, pages 82, 84, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Concave lenses; refraction of light, page 203, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 14:44, 3 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
A convex lens is a shaped piece of glass that is thickest at the centre and thinnest at the edges.
| A picture of a concave lens. | The symbol used in diagrams to represent a concave lens |
About Concave Lenses
- A concave lens causes parallel rays of light to diverge, so it can also be called a diverging lens.
- A concave lens cannot be used to focus light. However, they are used in glasses to correct the focussing of a lens in the eye.
- Concave lenses produce a virtual image.
Focal Length of a Concave Lens
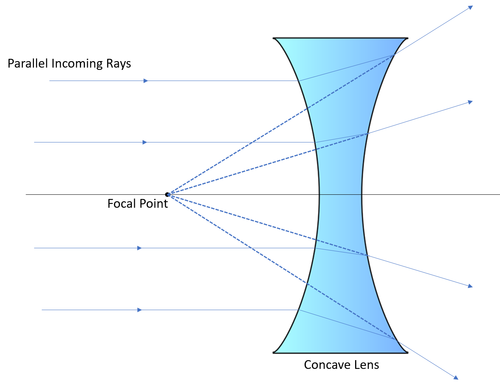
| A concave lens causes parallel rays to diverge. The focal point for the concave lens is on the same side of the lens as the object. |
- The focal length of a concave lens is the distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens. However, this cannot be measured through experiment.
Ray Diagrams
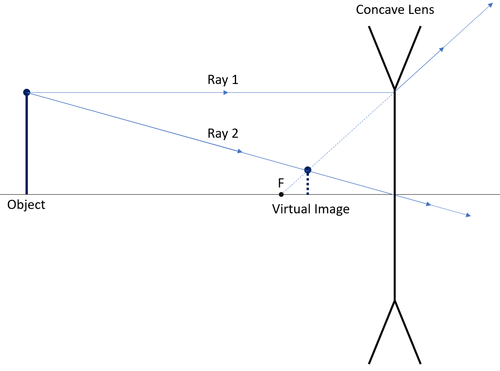
| A ray diagram for a concave lens.
In this diagram: "Ray 1" is traced backwards after being refracted by the lens. "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the lens. This ray is also traced backwards. The diagram shows that a diminished virtual image is produced at the point that the 'traced' lines from "ray 1" and "ray 2" cross one another. |
References
AQA
- Concave lenses, page 206, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Concave lenses, page 71, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Concave lenses, pages 208-211, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Concave lenses, pages 267, 268, 273, 274, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Concave lenses, pages 82, 84, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Concave lenses; refraction of light, page 203, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA