Ray Diagram
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Ray Diagram is a way to represent how light interacts with a boundary.
About Ray Diagrams
- A Ray Diagram shows how light rays travel in straight lines.
Ray Diagrams can be used to show:
- Diffuse Reflection - How we see objects.
- Specular Reflection - How we see images in shiny surfaces.
- Refraction - When light changes direction as it enters a new medium.
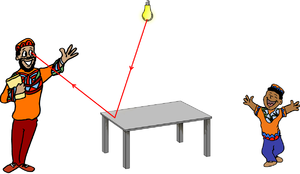
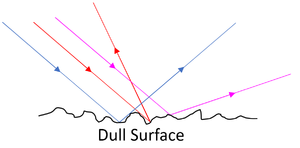
Diffuse Reflection
| Diffuse Reflection allows us to see objects as the light from a light source bounces off a surface into our eyes. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |
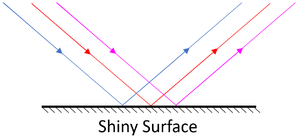
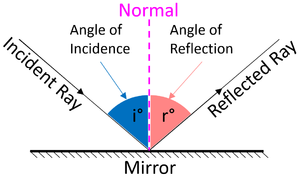
Specular Reflection
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Specular Reflection from a mirror can be seen to follow the Law of Reflection. |
Refraction
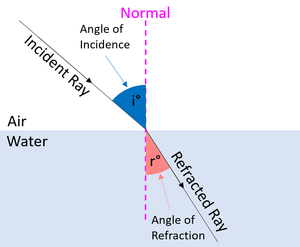
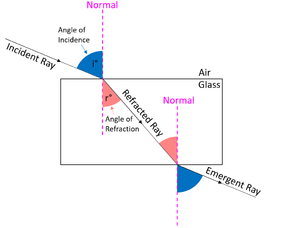
| When light enters a new medium it changes direction. | Light is refracted as it passes from one medium into another. |
Key Stage 4 Foundation
Meaning
A Ray Diagram is a way to represent how light is affected by the interface between to media.
About Ray Diagrams
- A Ray Diagram shows how light rays travel in straight lines.
Ray Diagrams can be used to show:
- Diffuse Reflection - How we see objects.
- Specular Reflection - How we see images in shiny surfaces.
- Refraction - When light changes direction as it enters a new medium.
Diffuse Reflection
| Diffuse Reflection allows us to see objects as the light from a light source bounces off a surface into our eyes. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |
Specular Reflection
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Specular Reflection from a mirror can be seen to follow the Law of Reflection. |
Refraction At a Flat Interface
| When light enters a new medium it changes direction. | Light is refracted as it passes from one medium into another. |
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
A Ray Diagram is a way to represent how light is affected by the interface between to media.
About Ray Diagrams
- A Ray Diagram shows how light rays travel in straight lines.
Ray Diagrams can be used to show:
- Diffuse Reflection - How we see objects.
- Specular Reflection - How we see images in shiny surfaces.
- Refraction - When light changes direction as it enters a new medium.
Diffuse Reflection
| Diffuse Reflection allows us to see objects as the light from a light source bounces off a surface into our eyes. | Diffuse Reflection happens from a rough surface. |
Specular Reflection
| Specular Reflection happens from a smooth surface. | Specular Reflection from a mirror can be seen to follow the Law of Reflection. |
Refraction At a Flat Interface
| When light enters a new medium it changes direction. | Light is refracted as it passes from one medium into another. |
Refraction at a Curved Interface
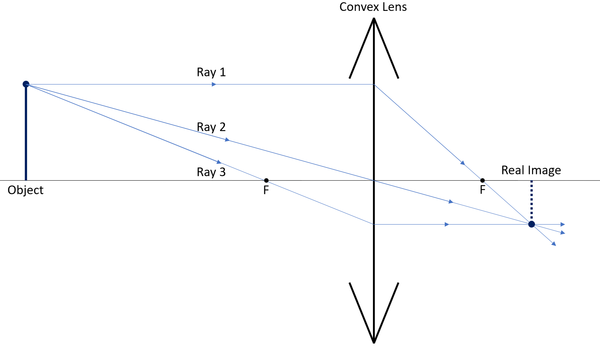
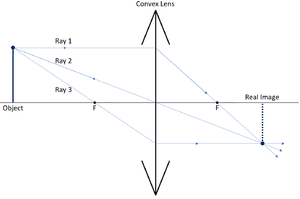
| A ray diagram for a convex lens.
In this diagram: "Ray 1" is shown crossing the focal point of the lens after being refracted. "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the lens. "Ray 3" is shown crossing the focal point before the lens. The diagram shows that a diminished real image is produced when the object distance is greater than the focal length of the convex lens. |
| Comparing these two diagrams shows that the image size increases as the object distance approaches the focal length of the lens. | |
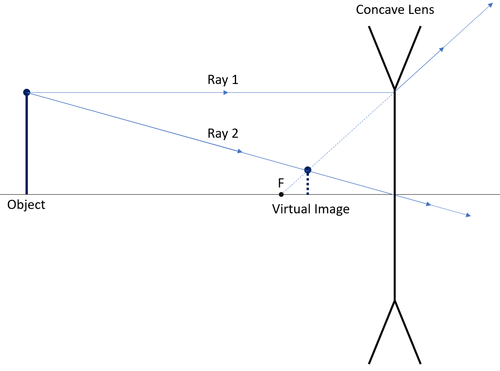
| A ray diagram for a concave lens.
In this diagram: "Ray 1" is traced backwards after being refracted by the lens. "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the lens. This ray is also traced backwards. The diagram shows that a diminished virtual image is produced at the point that the 'traced' lines from "ray 1" and "ray 2" cross one another. |
References
AQA
- Ray diagram, pages 191, 202-5, 215, 228-9, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Ray diagrams, page 222, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Ray diagrams, pages 195, 196, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Ray diagrams; for a concave lens, page 206, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Ray diagrams; for a convex lens, pages 204-6, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Ray diagrams; for a mirror, pages 188, 189, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Ray diagrams; lenses, pages 270-274, 276, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Ray diagrams; reflection, pages 235, 238, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Ray diagrams; refraction, pages 232, 233, 237, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Ray diagrams, pages 66-67, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; converging lenses, pages 122-124, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; diverging lenses, pages 125, 126, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; lenses, page 42, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; reflection, pages 115-117, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; refraction, pages 34, 39, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Ray diagrams; refraction, pages 99, 100, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel