Difference between revisions of "Hearing"
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
There are several parts of the ear you should know: | There are several parts of the ear you should know: | ||
*[[Pinna]] - The shaped [[cartilage]] collects the sound. | *[[Pinna]] - The shaped [[cartilage]] collects the sound. | ||
| − | *[[Ear | + | *[[Ear Canal]] - The tube leading to the [[Ear Drum|ear drum]]. |
*[[Ear Drum]] - This [[vibrate]]s like a drum skin when sound hits it. | *[[Ear Drum]] - This [[vibrate]]s like a drum skin when sound hits it. | ||
*[[Ossicles]] - Three tiny [[bone]]s that pass the [[Vibrate|vibration]] to the [[cochlea]]. | *[[Ossicles]] - Three tiny [[bone]]s that pass the [[Vibrate|vibration]] to the [[cochlea]]. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
There are several parts of the ear you should know: | There are several parts of the ear you should know: | ||
*[[Pinna]] - The shaped [[cartilage]] collects the sound. | *[[Pinna]] - The shaped [[cartilage]] collects the sound. | ||
| − | *[[Ear | + | *[[Ear Canal]] - The tube leading to the [[Ear Drum|ear drum]]. |
*[[Ear Drum]] - This [[vibrate]]s like a drum skin when sound hits it. | *[[Ear Drum]] - This [[vibrate]]s like a drum skin when sound hits it. | ||
*[[Ossicles]] - Three tiny [[bone]]s that pass the [[Vibrate|vibration]] to the [[cochlea]]. | *[[Ossicles]] - Three tiny [[bone]]s that pass the [[Vibrate|vibration]] to the [[cochlea]]. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
#The [[Ear Drum|ear drum]]s is connected to the [[ossicles]] which pass the [[vibration]] onto the [[cochlea]]. | #The [[Ear Drum|ear drum]]s is connected to the [[ossicles]] which pass the [[vibration]] onto the [[cochlea]]. | ||
#Tiny hairs in the [[cochlea]] are connected to [[Receptor Cell|receptor cells]] in the [[ear]]s which create an [[Action Potential|action potential]] which sends an [[Impulse (Biology)|impulse]] to the [[Central Nervous System|central nervous system (CNS)]]. | #Tiny hairs in the [[cochlea]] are connected to [[Receptor Cell|receptor cells]] in the [[ear]]s which create an [[Action Potential|action potential]] which sends an [[Impulse (Biology)|impulse]] to the [[Central Nervous System|central nervous system (CNS)]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Extra Information== | ||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LkGOGzpbrCk}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Hearing, page 183, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Hearing, page 104, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Hearing, pages 58-59, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:24, 20 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 1
Meaning
Hearing is what we sense with our ears.
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Hearing is one of the 5 main human senses.
About Hearing
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Hearing is a sense that allows animals detect sound.
About Hearing
- Animals hear with their ears.
- Hearing can be damaged by listening to loud sounds too often.
- The ears of different animals can hear different sounds. Some animals can hear sounds too high pitched for us to hear and some can hear sounds too low pitched for us to hear.
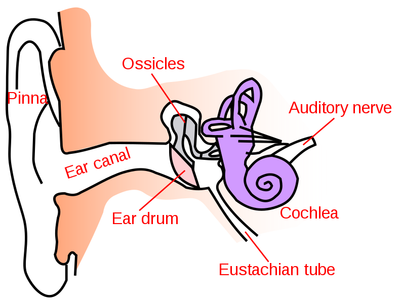
There are several parts of the ear you should know:
- Pinna - The shaped cartilage collects the sound.
- Ear Canal - The tube leading to the ear drum.
- Ear Drum - This vibrates like a drum skin when sound hits it.
- Ossicles - Three tiny bones that pass the vibration to the cochlea.
- Cochlea - A spiral tube with a liquid inside it and tiny hairs attached to nerve cells.
- Eustachian Tube - A tube used to keep the pressure the same both sides of the ear drum to stop it bursting.
- Auditory Nerve - The nerve connecting the ear to the brain.
| A diagram of the ear. |
- Sound travels into the ear canal where it causes the ear drum to vibrate.
- The ear drums is connected to the ossicles which pass the vibration onto the cochlea.
- Tiny hairs in the cochlea are connected to nerves that make an electrical signal which goes to the brain.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Hearing is a sense that allows animals detect sound.
About Hearing
- Animals hear with their ears.
- Hearing can be damaged by listening to loud sounds too often.
- The ears of different animals can hear different sounds. Some animals can hear sounds too high pitched for us to hear and some can hear sounds too low pitched for us to hear.
There are several parts of the ear you should know:
- Pinna - The shaped cartilage collects the sound.
- Ear Canal - The tube leading to the ear drum.
- Ear Drum - This vibrates like a drum skin when sound hits it.
- Ossicles - Three tiny bones that pass the vibration to the cochlea.
- Cochlea - A spiral tube with a liquid inside it and tiny hairs attached to nerve cells.
- Eustachian Tube - A tube used to keep the pressure the same both sides of the ear drum to stop it bursting.
- Auditory Nerve - The nerve connecting the ear to the brain.
| A diagram of the ear. |
- Sound travels into the ear canal where it causes the ear drum to vibrate.
- The ear drums is connected to the ossicles which pass the vibration onto the cochlea.
- Tiny hairs in the cochlea are connected to receptor cells in the ears which create an action potential which sends an impulse to the central nervous system (CNS).