Difference between revisions of "Permanent Magnet"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac357 ''Permanent magnets, page 92, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac357 ''Permanent magnets, page 92, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Permanent magnets, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Permanent magnets, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Permanent magnets, page 168, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Permanent magnets, page 267, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 02:20, 27 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A permanent magnet is an object with its own magnetic field that remains there even when there are no other external magnetic fields.
About Permanent Magnets
- A bar magnet is a permanent magnet.
- Permanent magnets are used in a electrical motors.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A permanent magnet is an object with its own magnetic field that remains there even when there are no other external magnetic fields.
About Permanent Magnets
- A bar magnet is a permanent magnet.
- Permanent magnets are used in a electrical motors.
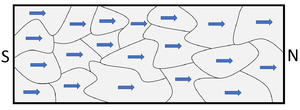
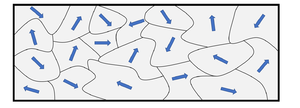
- A magnet is made of several small magnetic domains which are regions in the magnet which act as smaller magnets. In a permanent magnet these magnetic domains are fixed in place and need energy to change their magnetic direction.
- A permanent magnet can only lose its magnetic field under certain conditions:
- When it is struck with a sudden force.
- When it is heated.
- When an extremely strong external magnetic field is applied.
| When magnetic domains are aligned the object has its own magnetic field so it acts like a magnet. | When the magnetic domains are not aligned it does not have a magnetic field because the effect of the magnetic domains cancels out. |
References
AQA
- Permanent magnet, pages 242, 245, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 223, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 229, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Permanent magnets, page 92, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Permanent magnets, pages 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA