D.C. Motor
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

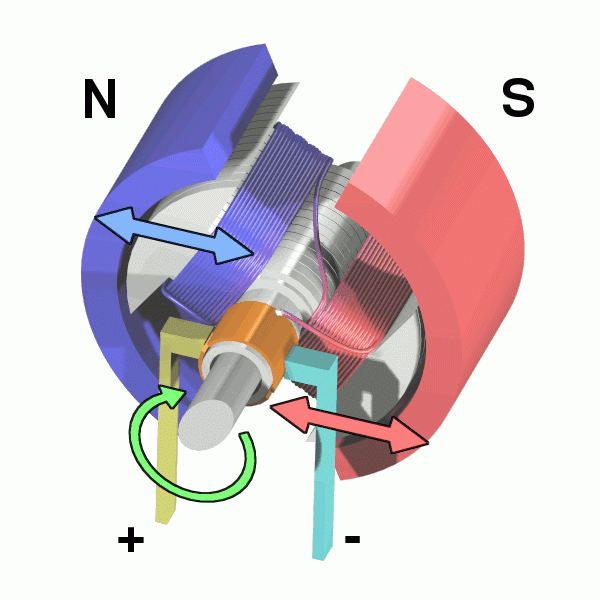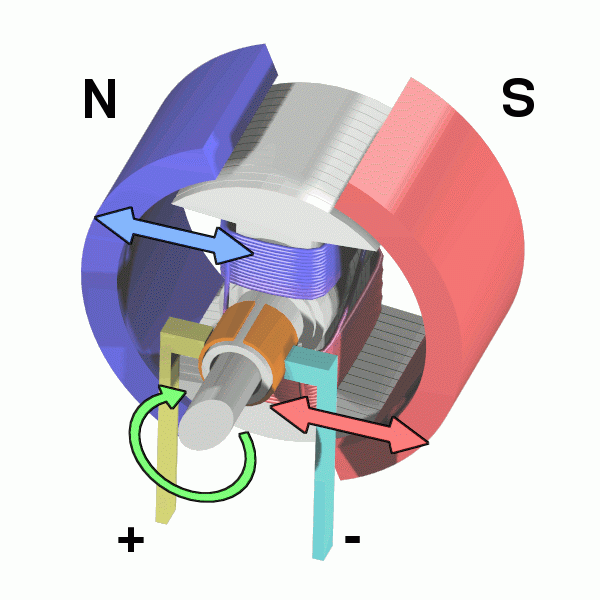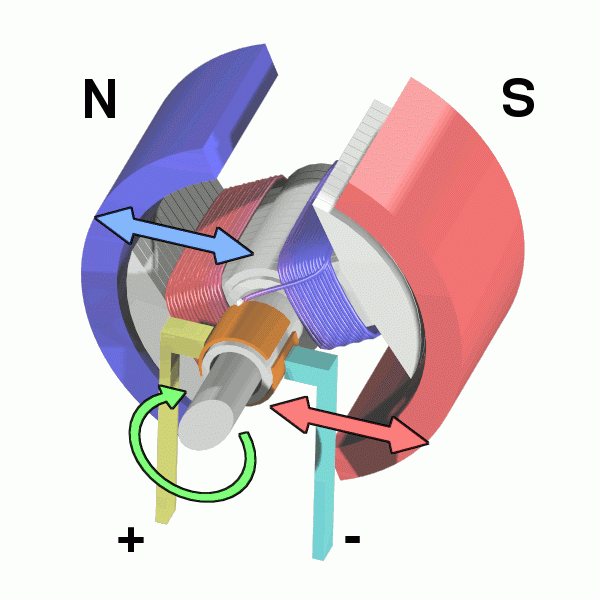
A typical D.C. Motor.
A D.C. Motor is an electrical motor which uses an electromagnet and permanent magnets to spin an axle.
About D.C. Motors
- The D.C. stands for Direct Current because the motor uses a Direct Current to work which means it can be powered by a cell or battery.
- When a current passes through the electromagnet in the d.c. motor the electromagnet is attracted to one of the permanent magnets in the motor. This causes the electromagnet to move.
| A D.C. Motor spinning due to a current passing through the electromagnets. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning

A typical D.C. Motor.
A D.C. Motor is an electrical motor which uses an electromagnet and permanent magnets to spin an axle.
About D.C. Motors
- The D.C. stands for Direct Current because the motor uses a Direct Current to work which means it can be powered by a cell or battery.
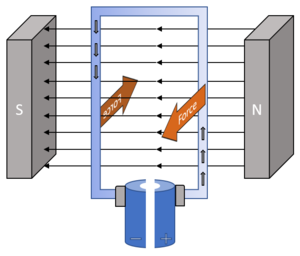
- The D.C. Motor uses the motor effect to cause a rotation of the axle.
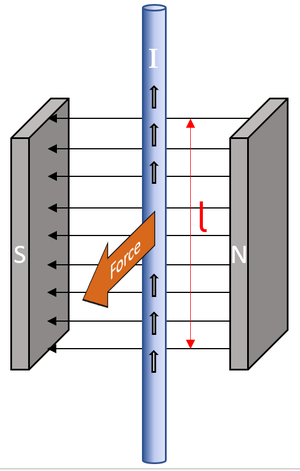
| The direction on the force on this wire can be found using Fleming's Left Hand Rule. | In a D.C. Motor there is one or more coils of wire in the magnetic field. The current through one part of the wire causes it to move in the opposite direction to the other side of the wire. This causes the coil to spin. |
- A D.C. Motor has a split ring which means that when the coil has made a half rotation the current through the coil changes direction so that the current always goes in the same direction in the left part of the coil and always goes in the same direction on the right part of the coil.
- The force that can be applied by the motor depends upon:
| A D.C. Motor spinning due to a current passing through the electromagnets. |