Motor Effect
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
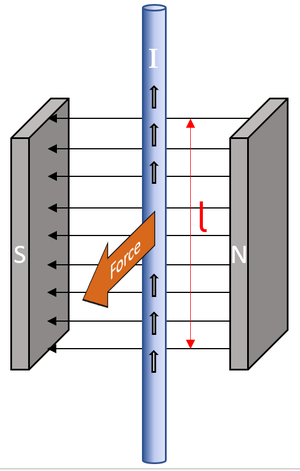
The motor effect is the force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field.
About The Motor Effect
- When an a wire has an electrical current it has a magnetic field. If this wire is in the presence of an external magnetic field the two fields will interact causing a force.
- The magnitude of the force depends upon:
- The Current - The greater the current the greater the force.
- The Magnetic Field - The greater the strength of magnetic field the greater the force.
- The force on a current carrying wire is at right angles to both the current and the magnetic field.
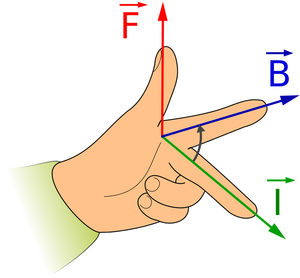
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule can be used to find the direction of the force.
|
\(\overrightarrow{B}\): First finger field. \({I}\): Second finger current. \(\overrightarrow{F}\): The force. |
The direction on the force on this wire can be found using Fleming's Left Hand Rule. |
Equation
Force = (Magnetic Flux Density) x (Current) x (Length)
\(F = BIl\)
Where
\(B\) = The Magnetic Flux Density (strength of magnetic field).
\(I\) = The Electrical Current through the wire.
\(l\) = The length of wire inside the magnetic field.
\(F\) = The force on the wire.
Example Calculations
| A wire carrying a current of 2.3A is inside a 55mT magnetic field that extends along the wire by a length of 6.1cm. Calculate the force on the wire correct to two significant figures. | 23cm of wire carrying 1.2A of current is contained in a 37mT magnetic field. Calculate the force on the wire correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(B\) = 55mT = 55x10-3T \(I\) = 2.3A \(l\) = 6.1cm = 6.1x10-2m |
1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(B\) = 37mT = 37x10-3T \(I\) = 1.2A \(l\) = 23cm = 23x10-2m |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(F = BIl\) \(F = 55\times 10^{-3} \times 2.3 \times 6.1 \times 10^{-2}\) \(F = 7.7165 \times 10^{-3}N\) \(F \approx 7.7\times 10^{-3}N\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(F = BIl\) \(F = 37\times 10^{-3} \times 1.2 \times 23 \times 10^{-2}\) \(F = 1.0212 \times 10^{-2}N\) \(F \approx 1.0\times 10^{-2}N\) |
References
AQA
- Motor effect, page 228, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Motor effect, page 249, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 220-221, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 221-227, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 281, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 295-302, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 94, 95, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 172, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 406, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Motor effect, pages 273-278, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Motor effect, pages 87, 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel