Difference between revisions of "Inner Core"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
: The '''inner core''' is [[solid]]. | : The '''inner core''' is [[solid]]. | ||
: The '''inner core''' spins due to [[Convection Current|convection currents]] in the [[Outer Core|outer core]] which generates the [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | : The '''inner core''' spins due to [[Convection Current|convection currents]] in the [[Outer Core|outer core]] which generates the [[Earth]]'s [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Inner core, Earth, pages 244-245, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:23, 13 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
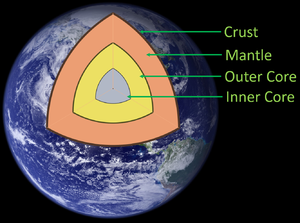
The inner core is the inner most layer of the Earth underneath the outer core.
About the Inner Core
- The inner core is solid.
- The inner core spins due to convection currents in the outer core which generates the Earth's magnetic field.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The inner core is the inner most layer of the Earth underneath the outer core.
About the Inner Core
- The inner core is solid.
- The inner core spins due to convection currents in the outer core which generates the Earth's magnetic field.