Difference between revisions of "Gas Pressure"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|- | |- | ||
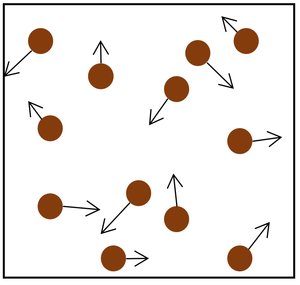
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Particle Model|particle model]] of a [[gas]] showing the particles as red balls and their speed and direction shown by the arrows. The longer the arrows the faster they are moving. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Particle Model|particle model]] of a [[gas]] showing the particles as red balls and their speed and direction shown by the arrows. The longer the arrows the faster they are moving. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | : The '''gas pressure''' can be increased in two ways. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GasPressure2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:GasPressure3.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
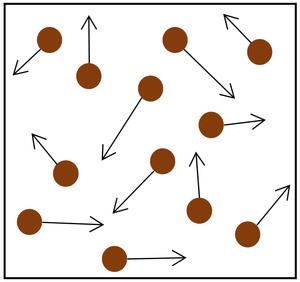
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Increasing the [[temperature]] of the [[gas]] which makes the [[particle]]s move faster. This causes the particles to hit the walls of the container more often and with a greater [[force]]. | ||
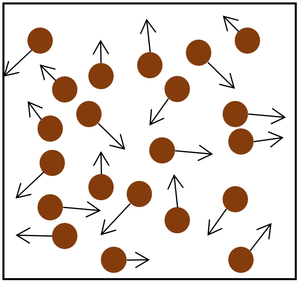
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Increasing the number of particles in the container. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 22 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gas pressure is the pressure on an object caused by a gas.
About Gas Pressure
| The particle model of a gas showing the particles as red balls and their speed and direction shown by the arrows. The longer the arrows the faster they are moving. |
- The gas pressure can be increased in two ways.
| Increasing the temperature of the gas which makes the particles move faster. This causes the particles to hit the walls of the container more often and with a greater force. | Increasing the number of particles in the container. |