Difference between revisions of "Indicator (Chemistry)"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: Different '''indicators''' will have a different range of colours for different [[pH]] values. | : Different '''indicators''' will have a different range of colours for different [[pH]] values. | ||
: A good '''indicator''' can be added to [[solution]] without affecting the [[pH]] of the [[solution]]. If an '''indicator''' change the [[pH]] of a [[solution]] it could not give an [[accurate]] [[reading]]. | : A good '''indicator''' can be added to [[solution]] without affecting the [[pH]] of the [[solution]]. If an '''indicator''' change the [[pH]] of a [[solution]] it could not give an [[accurate]] [[reading]]. | ||
| + | Some '''indicators''' you should know: | ||
| + | *[[Litmus Paper]] | ||
| + | *[[Red Cabbage Indicator]] | ||
| + | *[[Universal Indicator]] | ||
| + | *[[Phenolphthalein]] | ||
| + | *[[Methyl Organge]] | ||
| + | *[[Bromothymol Blue]] | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
Revision as of 08:39, 29 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
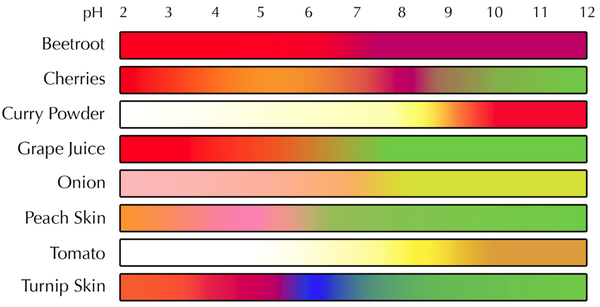
An indicator is a dye that changes colour depending on the pH of a solution.
About Indicators
- The colour of an indicator can be used to tell the pH of a solution.
- Different indicators will have a different range of colours for different pH values.
- A good indicator can be added to solution without affecting the pH of the solution. If an indicator change the pH of a solution it could not give an accurate reading.
Some indicators you should know:
- Litmus Paper
- Red Cabbage Indicator
- Universal Indicator
- Phenolphthalein
- Methyl Organge
- Bromothymol Blue