Difference between revisions of "Parallel Circuit"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|[[File:CircuitCellMotorResistorSeries.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:CircuitCellMotorResistorSeries.png|center|200px]] | ||
|[[File:CircuitCellMotorResistorBulbSeries.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:CircuitCellMotorResistorBulbSeries.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:CircuitDiagramCellBulbAmmeterSeries.png|center|200px]] | ||
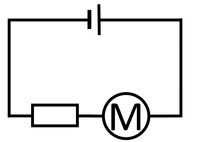
| + | |[[File:CircuitDiagramCellMotorResistorSeries.png|center|200px]] | ||
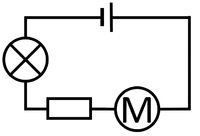
| + | |[[File:CircuitDiagramCellMotorResistorBulbSeries.png|center|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
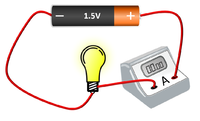
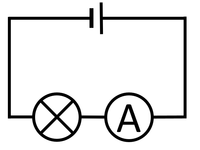
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Electrical Bulb|bulb]] and [[Ammeter]] are in [[Series Circuit|series]] so they have the same [[Electrical Current|Current]] going through them. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Electrical Bulb|bulb]] and [[Ammeter]] are in [[Series Circuit|series]] so they have the same [[Electrical Current|Current]] going through them. | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 31 October 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
- In a paralle circuit the current is split at the junctions.
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same Potential Difference across them.
Examples
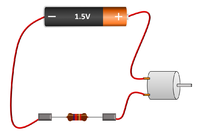
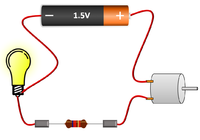
| The bulb and Ammeter are in series so they have the same Current going through them. | The motor and resistor are in series so they have the same Current passing through them but share the 1.5V Potential Difference between them. | The motor, resistor and bulb are in series so they all have the same Current passing through them but share the 1.5V Potential Difference between them. |