Difference between revisions of "Pancreas"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===The Pancreas as an Endocrine Gland=== | ===The Pancreas as an Endocrine Gland=== | ||
| − | : The [[pancreas]] | + | : The [[pancreas]] [[secrete]]s the [[hormone]]s [[insulin]] and [[glucagon]] to regulate [[Blood Glucose|blood glucose]] levels. |
| + | : The [[liver]] is a [[Target Organ|target organ]] for the [[hormone]] [[glucagon]]. | ||
: In [[Diabetes Type 1]] the [[pancreas]] is damaged and cannot produce [[insulin]] to regulate [[Blood Glucose|blood glucose]] levels. | : In [[Diabetes Type 1]] the [[pancreas]] is damaged and cannot produce [[insulin]] to regulate [[Blood Glucose|blood glucose]] levels. | ||
: In [[Diabetes Type 2]] the [[pancreas]] may be overworked having to produce much more [[insulin]] than it would in a healthy [[animal]]. | : In [[Diabetes Type 2]] the [[pancreas]] may be overworked having to produce much more [[insulin]] than it would in a healthy [[animal]]. | ||
Revision as of 12:33, 15 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
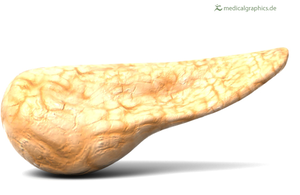
A computer generated image of a pancreas.
The pancreas is an organ in the Digestive System and an endocrine gland.
The Pancreas and Digestion
- The pancreas produces digestive enzymes including pancreatic amylase, trypsin (which is a type of protease and lipase.
- The digestive enzymes are passed down the pancreatic duct which joins with the bile duct before arriving in the Small Intestine.
The Pancreas as an Endocrine Gland
- The pancreas secretes the hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels.
- The liver is a target organ for the hormone glucagon.
- In Diabetes Type 1 the pancreas is damaged and cannot produce insulin to regulate blood glucose levels.
- In Diabetes Type 2 the pancreas may be overworked having to produce much more insulin than it would in a healthy animal.