Difference between revisions of "Evolution by Natural Selection"
(→Meaning) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
===About Evolution by Natural Selection=== | ===About Evolution by Natural Selection=== | ||
| − | : Evolution is caused by two important factors; [[variation]] and [[heredity]]. | + | : '''Evolution by natural selection''' is caused by two important factors; [[variation]] and [[heredity]]. |
: A species will have [[variation]] between [[organism]]s in the [[population]]. This means they will all be slightly different. | : A species will have [[variation]] between [[organism]]s in the [[population]]. This means they will all be slightly different. | ||
: Some [[variation]]s are [[heredity|hereditary]] which means they are passed on from parent to [[offspring]]. | : Some [[variation]]s are [[heredity|hereditary]] which means they are passed on from parent to [[offspring]]. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:900px; text-align:center;" |This picture shows a series of human skulls starting on the left with a skull from 20 million years ago through to a modern human skull. | | style="height:20px; width:900px; text-align:center;" |This picture shows a series of human skulls starting on the left with a skull from 20 million years ago through to a modern human skull. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Evolution by natural selection''' is the process that leads to new [[species]] being formed over thousands of generations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Evolution by Natural Selection=== | ||
| + | : '''Evolution by natural selection''' is caused by two important factors; [[variation]] and [[heredity]]. | ||
| + | : A [[species]] will have [[variation]] between [[organism]]s in the [[population]]. This means they will all be slightly different. | ||
| + | : Some [[variation]]s are [[heredity|hereditary]] which means they are passed on from parent to [[offspring]]. | ||
| + | : If a [[heredity|heritable]] [[variation]] gives a member of the [[species]] an advantage over the others in its environment, then it is more likely to survive and [[Reproduction|reproduce]]. This is [[Natural Selection|natural selection]] where some [[variation]]s cause [[organism]]s to die while other [[variation]]s cause [[organism]]s to have more [[offspring]]. | ||
| + | : [[Variation]] can be caused by random [[mutation]]s which occur during [[reproduction]]. If that [[mutation]] provides an advantage to that [[organism]] over others in the [[species]] then it will have more [[offspring]] than others spreading that beneficial [[mutation]]. Over several [[generation]]s that [[mutation]] will be spread throughout the [[species]]. Over time many of these [[mutation]]s occur changing the entire [[population]] until they are no longer the same [[species]] as they were prior to these [[mutation]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Development of the Theory of Evolution=== | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 19 November 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Evolution means a change over time. All species on earth evolve.
About Evolution
- The different types of creatures we see today looked different millions of years ago. The creatures have evolved.
- A single animal or plant does not evolve. A whole population evolves over many generations.
- Evolution can be shown by looking at fossils of creatures that lived millions of years ago.
Examples
| The giraffe used to have a short neck. Over many generations the population of giraffes had longer and longer necks. |
| Arctic Fox | Desert Fox |
| The Arctic Fox has evolved to have thick white fur and small ears. | The Desert Fox has evolved to have thin sandy coloured fur and very large ears. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Evolution by natural selection is the process by which new species are formed over thousands of generations.
About Evolution by Natural Selection
- Evolution by natural selection is caused by two important factors; variation and heredity.
- A species will have variation between organisms in the population. This means they will all be slightly different.
- Some variations are hereditary which means they are passed on from parent to offspring.
- If a heritable variation gives a member of the species an advantage over the others in its environment, then it is more likely to survive and reproduce. This is natural selection where some variations cause organisms to die while other variations cause organisms to have more offspring.
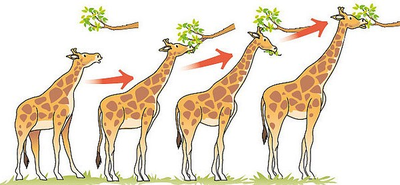
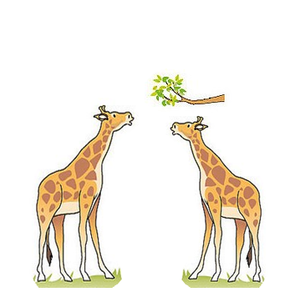
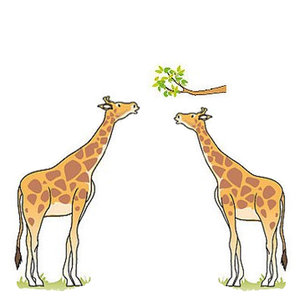
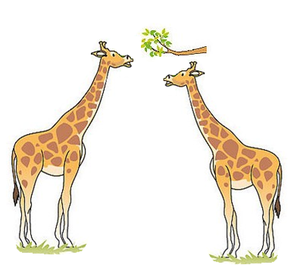
| Millions of years ago all Giraffes had short necks. Variation meant some Giraffes were a little bit taller than others. Those Giraffes could get to the higher leaves in trees. This meant they could eat more. The shorter Giraffes couldn't get enough food and died. So the taller Giraffes survived and their offspring inherited their slightly longer necks. | After a few generations all the giraffes had slightly longer necks, but because of variation some had even longer necks still. This meant they they were more likely to get food, survive and have children than the shorter giraffes. So their offspring inherited these even longer necks. |
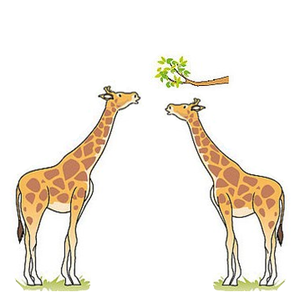
| This process of evolution repeated again and again. | Millions of years later, after many generations, eventually all the Giraffe had very long necks. |
| This picture shows a series of human skulls starting on the left with a skull from 20 million years ago through to a modern human skull. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Evolution by natural selection is the process that leads to new species being formed over thousands of generations.
About Evolution by Natural Selection
- Evolution by natural selection is caused by two important factors; variation and heredity.
- A species will have variation between organisms in the population. This means they will all be slightly different.
- Some variations are hereditary which means they are passed on from parent to offspring.
- If a heritable variation gives a member of the species an advantage over the others in its environment, then it is more likely to survive and reproduce. This is natural selection where some variations cause organisms to die while other variations cause organisms to have more offspring.
- Variation can be caused by random mutations which occur during reproduction. If that mutation provides an advantage to that organism over others in the species then it will have more offspring than others spreading that beneficial mutation. Over several generations that mutation will be spread throughout the species. Over time many of these mutations occur changing the entire population until they are no longer the same species as they were prior to these mutations.