Difference between revisions of "Thermal Decomposition"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== Thermal Decomposition is a type of chemical reaction in which a large compound is broken down into smaller molecu...") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
: Copper Carbonate → Copper Oxide + Carbon Dioxide | : Copper Carbonate → Copper Oxide + Carbon Dioxide | ||
: Zinc Carbonate → Zinc Oxide + Carbon Dioxide | : Zinc Carbonate → Zinc Oxide + Carbon Dioxide | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Experiment=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ThermalDecompositionDiagram.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
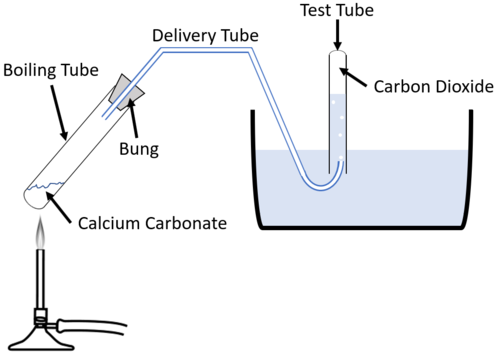
| + | : 1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram using 20g of metal carbonate in the [[Boiling Tube]]. | ||
| + | : 2. Use a [[Clamp Stand]] to hold the [[Boiling Tube]] in place. | ||
| + | : 3. Place the [[Test Tube]] underwater to fill and hold upside down over the exit of the delivery tube. | ||
| + | : 4. Heat the metal carbonate in the [[Boiling Tube]]. | ||
| + | : 5. Observe any colour change of the [[substance]] in the [[Boiling Tube]] and collect the [[gas]] to test whether it is [[Carbon Dioxide]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Thermal decomposition, page 153, 194, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Thermal decomposition, page 178, 226, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Thermal decomposition, page 69, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10353 ''Thermal decomposition, pages 134, 149, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Thermal decomposition, pages 182, 232, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d258 ''Thermal decomposition, pages 61, 72, 77, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Thermal decomposition, pages 97, 102, 110-1, 123, 236, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Thermal decomposition; of sodium hydrogen carbonate, pages 188-9, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:35, 13 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Thermal Decomposition is a type of chemical reaction in which a large compound is broken down into smaller molecules due to high temperatures.
About Thermal Decomposition
- When materials are heated the particles inside vibrate and move more quickly, colliding with one another. For large molecules this can cause them to collide with enough force to break the molecule apart into smaller molecules. This is thermal decomposition.
- Thermal Decomposition happens to certain types of compound more than others. At this stage the thermal decompositions you should know have the general equation: Metal Carbonate → Metal Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
Examples
Metal Carbonate → Metal Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
- Calcium Carbonate → Calcium Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
- Copper Carbonate → Copper Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
- Zinc Carbonate → Zinc Oxide + Carbon Dioxide
Experiment
|
References
AQA
- Thermal decomposition, page 153, 194, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, page 178, 226, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, page 69, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, pages 134, 149, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, pages 182, 232, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, pages 61, 72, 77, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermal decomposition, pages 97, 102, 110-1, 123, 236, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Thermal decomposition; of sodium hydrogen carbonate, pages 188-9, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA