Difference between revisions of "Frequency"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== Frequency is the number of waves that pass by in one second.") |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Frequency]] is the number of [[wave]]s that pass by in one [[second]]. | [[Frequency]] is the number of [[wave]]s that pass by in one [[second]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Frequency=== | ||
| + | : [[Frequency]] is [[measure]]d in [[Hertz]] (Hz). | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Water Waves''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:WaveFrequency.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
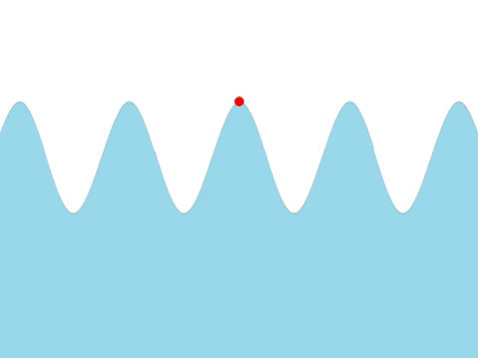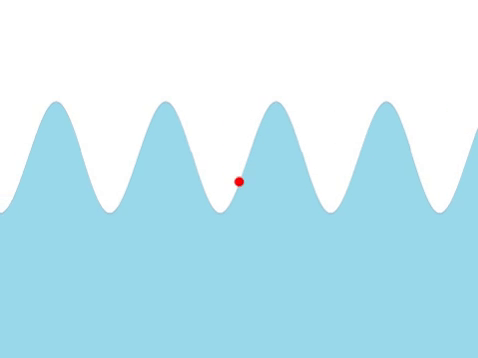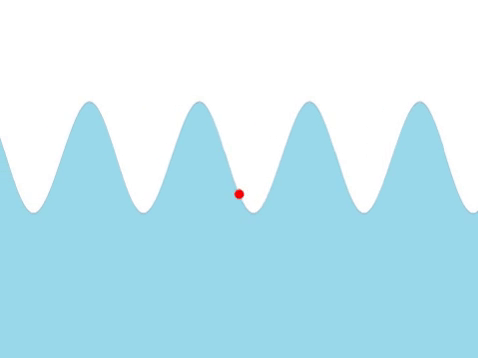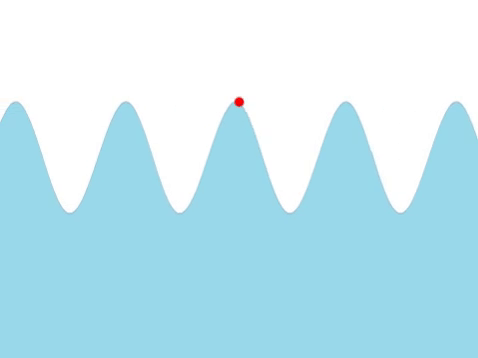
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[frequency]] of this [[wave]] can be found by counting the number of times the red marker [[oscillate]]s every [[second]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : The higher the [[frequency]] the quicker the [[wave]] [[Oscillation|oscillates]]. | ||
| + | : In [[sound]] [[frequency]] is known as [[pitch]]. A high [[pitch]] is a high [[frequency]]. | ||
| + | : In [[light]] [[frequency]] affects the [[colour]] of the [[light]]. Red is a low [[frequency]] and violet is a high [[frequency]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Equation=== | ||
| + | Frequency = 1/(Period) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{1}{T}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where: | ||
| + | |||
| + | f = [[Frequency]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | T = [[Period|time period]] (the [[time]] it takes for one [[wave]] to pass a point). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Frequency]] is the number of [[wave]]s that pass a given point in one [[second]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Frequency=== | ||
| + | : [[Frequency]] is a [[scalar]] quantity because it has [[magnitude]] but no direction. | ||
| + | : The [[SI Unit]] of [[frequency]] is [[Hertz]] (Hz). | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Water Waves''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:WaveFrequency.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[frequency]] of this [[wave]] can be found by counting the number of times the red marker [[oscillate]]s every [[second]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : The higher the [[frequency]] the quicker the [[wave]] [[Oscillation|oscillates]]. | ||
| + | : In [[sound]] [[frequency]] is known as [[pitch]]. A high [[pitch]] is a high [[frequency]]. | ||
| + | : In [[light]] [[frequency]] affects the [[colour]] of the [[light]]. Red is a low [[frequency]] and violet is a high [[frequency]]. | ||
| + | : When [[wave]] enters a new [[medium]] it will remain the same [[frequency]] but the [[Wave Speed|wave speed]] and [[wavelength]] will change. | ||
| + | : [[Frequency]] can be found by counting the number of [[wave]]s which pass a point in a given [[time]] and dividing this by the [[time]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Equation=== | ||
| + | ====Equation 1==== | ||
| + | ''NB: You do not need to remember this equation but you should know how to find [[frequency]] given the [[time]] taken for one [[wave]] to pass a point.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frequency = 1/(Period) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{1}{T}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where: | ||
| + | f = [[Frequency]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | T = [[Period|time period]] (the [[time]] it takes for a wave to pass a point). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Equation 2==== | ||
| + | ''NB: You do not need to remember this equation but you should know how to find [[frequency]] given the number of [[wave]]s passing a point and the [[time]] taken.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frequency = (Number of Waves which pass a point)/(Time taken for waves to pass a point) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{n}{t}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where: | ||
| + | f = [[Frequency]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | n = Number of [[wave]]s which pass a point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | t = The [[time]] taken for those [[wave]]s to pass a point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Equation 3==== | ||
| + | ''NB: You should remember this equation with v as the subject of the formula.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Frequency = (Wave Speed)/(Wavelength) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{v}{\lambda}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> \lambda</math> = The [[wavelength]] of the [[wave]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>v</math> = The [[Wave Speed|wave speed]] of the [[wave]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f</math> = The [[frequency]] of the [[wave]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | ====Finding Frequency from Time Period==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |Calculate the [[frequency]] of a [[wave]] with a [[period]] of 0.04 seconds. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A giant pendulum takes 16 seconds to make one complete [[oscillation]]. Calculate the [[frequency]] of the pendulum. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | T = 0.04s | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | T = 16s | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{1}{T}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{1}{0.04}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = 25Hz</math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{1}{T}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{1}{16}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = 0.0625Hz</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finding Frequency from the number of waves and time taken==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A scientist wants to determine the [[frequency]] of a pendulum. They count that the pendulum [[oscillate]]s 15 times over 20 seconds. Calculate the [[frequency]] of the pendulum. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A sailor notices a buoy bounce up and down 24 times over a minute. Calculate the [[frequency]] of the [[wave]]s. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | n = 15 | ||
| + | |||
| + | t = 20s | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | n = 24 | ||
| + | |||
| + | t = 60 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{n}{t}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{15}{20}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = 0.75Hz</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{n}{t}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = \frac{24}{60}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>f = 0.4Hz</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Finding Frequency from Wavelength and Wave Speed==== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[microwave]] travelling at a speed of 3.0x10<sup>8</sup>m/s has a [[wavelength]] of 0.051m. Calculate the [[frequency]] of the [[wave]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |An [[ultrasound]] [[wave]] of [[wavelength]] 0.125m passes through an [[Iron]] block at a [[speed]] of 5000m/s. Calculate the [[frequency]] of the [[wave]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | v = 3.0x10<sup>8</sup>m/s | ||
| + | |||
| + | λ = 0.051m | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | v = 5000m/s | ||
| + | |||
| + | λ = 0.125m | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{v}{\lambda}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{3.0 \times 10^8}{0.051}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = 5882352941Hz</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f \approx 5900000000Hz</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{v}{\lambda}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = \frac{5000}{0.125}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> f = 40000Hz</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Frequency (f), pages 50-1, 583, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac201 ''Frequency, page 73, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Frequency, pages 189, 190, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Frequency, pages 190-3, 200-1, 206-9, 213-15, 218, 222, 224, 236-7, 275, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Frequency, pages 226, 227, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Frequency, pages 257, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Frequency; human hearing range, page 280, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac202 ''Frequency; human hearing range, page 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Frequency; Measurement of, pages 260, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Frequency; of EM waves, pages 200, 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Frequency; of EM waves, pages 242, 245, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac203 ''Frequency; of EM waves, pages 76, 81, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Frequency; of mains electricity, page 66, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac204 ''Frequency; of mains supply, page 31, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Frequency; of mains supply, page 86, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Frequency; of mains supply, page 89, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Frequency; table, pages 40-1, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Frequency (waves), page 91, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Frequency (waves); of hearing, page 104, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Frequency (waves); of infrasound, page 109, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Frequency (waves); of ultrasound, page 106, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Frequency, pages 164-166, 168, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Frequency, pages 32-34, 43, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Frequency, pages 331, 340, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Frequency, pages 49, 72, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Frequency, pages 137, 142, 149, , 153, 179, 256-157, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Frequency, pages 186-188, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945687/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945687&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a598e52189317a20311d7a632747bc9 ''Frequency, pages 59-61, 64, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:19, 11 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Frequency is the number of waves that pass by in one second.
About Frequency
| Water Waves |
| The frequency of this wave can be found by counting the number of times the red marker oscillates every second. |
- The higher the frequency the quicker the wave oscillates.
- In sound frequency is known as pitch. A high pitch is a high frequency.
- In light frequency affects the colour of the light. Red is a low frequency and violet is a high frequency.
Equation
Frequency = 1/(Period)
\(f = \frac{1}{T}\)
Where:
f = Frequency
T = time period (the time it takes for one wave to pass a point).
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Frequency is the number of waves that pass a given point in one second.
About Frequency
- Frequency is a scalar quantity because it has magnitude but no direction.
- The SI Unit of frequency is Hertz (Hz).
| Water Waves |
| The frequency of this wave can be found by counting the number of times the red marker oscillates every second. |
- The higher the frequency the quicker the wave oscillates.
- In sound frequency is known as pitch. A high pitch is a high frequency.
- In light frequency affects the colour of the light. Red is a low frequency and violet is a high frequency.
- When wave enters a new medium it will remain the same frequency but the wave speed and wavelength will change.
- Frequency can be found by counting the number of waves which pass a point in a given time and dividing this by the time.
Equation
Equation 1
NB: You do not need to remember this equation but you should know how to find frequency given the time taken for one wave to pass a point.
Frequency = 1/(Period)
\(f = \frac{1}{T}\)
Where: f = Frequency
T = time period (the time it takes for a wave to pass a point).
Equation 2
NB: You do not need to remember this equation but you should know how to find frequency given the number of waves passing a point and the time taken.
Frequency = (Number of Waves which pass a point)/(Time taken for waves to pass a point)
\(f = \frac{n}{t}\)
Where: f = Frequency
n = Number of waves which pass a point.
t = The time taken for those waves to pass a point.
Equation 3
NB: You should remember this equation with v as the subject of the formula.
Frequency = (Wave Speed)/(Wavelength)
\( f = \frac{v}{\lambda}\)
Where
\( \lambda\) = The wavelength of the wave.
\(v\) = The wave speed of the wave.
\(f\) = The frequency of the wave.
Example Calculations
Finding Frequency from Time Period
| Calculate the frequency of a wave with a period of 0.04 seconds. | A giant pendulum takes 16 seconds to make one complete oscillation. Calculate the frequency of the pendulum. |
| 1. State the known quantities
T = 0.04s |
1. State the known quantities
T = 16s |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\( f = \frac{1}{T}\) \( f = \frac{1}{0.04}\) \( f = 25Hz\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\( f = \frac{1}{T}\) \( f = \frac{1}{16}\) \( f = 0.0625Hz\) |
Finding Frequency from the number of waves and time taken
| A scientist wants to determine the frequency of a pendulum. They count that the pendulum oscillates 15 times over 20 seconds. Calculate the frequency of the pendulum. | A sailor notices a buoy bounce up and down 24 times over a minute. Calculate the frequency of the waves. |
| 1. State the known quantities
n = 15 t = 20s |
1. State the known quantities
n = 24 t = 60 |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(f = \frac{n}{t}\) \(f = \frac{15}{20}\) \(f = 0.75Hz\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(f = \frac{n}{t}\) \(f = \frac{24}{60}\) \(f = 0.4Hz\) |
Finding Frequency from Wavelength and Wave Speed
| A microwave travelling at a speed of 3.0x108m/s has a wavelength of 0.051m. Calculate the frequency of the wave correct to two significant figures. | An ultrasound wave of wavelength 0.125m passes through an Iron block at a speed of 5000m/s. Calculate the frequency of the wave correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities
v = 3.0x108m/s λ = 0.051m |
1. State the known quantities
v = 5000m/s λ = 0.125m |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\( f = \frac{v}{\lambda}\) \( f = \frac{3.0 \times 10^8}{0.051}\) \( f = 5882352941Hz\) \( f \approx 5900000000Hz\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\( f = \frac{v}{\lambda}\) \( f = \frac{5000}{0.125}\) \( f = 40000Hz\) |
References
AQA
- Frequency (f), pages 50-1, 583, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Frequency, page 73, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Frequency, pages 189, 190, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Frequency, pages 190-3, 200-1, 206-9, 213-15, 218, 222, 224, 236-7, 275, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Frequency, pages 226, 227, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Frequency, pages 257, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Frequency; human hearing range, page 280, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; human hearing range, page 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; Measurement of, pages 260, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Frequency; of EM waves, pages 200, 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; of EM waves, pages 242, 245, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; of EM waves, pages 76, 81, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; of mains electricity, page 66, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Frequency; of mains supply, page 31, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; of mains supply, page 86, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; of mains supply, page 89, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Frequency; table, pages 40-1, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Frequency (waves), page 91, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency (waves); of hearing, page 104, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency (waves); of infrasound, page 109, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency (waves); of ultrasound, page 106, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency, pages 164-166, 168, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency, pages 32-34, 43, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Frequency, pages 331, 340, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Frequency, pages 49, 72, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel