Difference between revisions of "Convex Lens"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 3== ===Meaning=== A '''convex''' lens is a shaped piece of glass that is thicker at the centre and thinner at the edges.") |
(→Finding the Focal Length) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
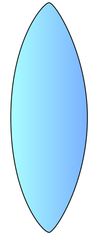
| − | A '''convex''' [[lens]] is a shaped piece of [[glass]] that is | + | A '''convex''' [[lens]] is a shaped piece of [[glass]] that is thickest at the centre and thinnest at the edges. |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLens.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLensSymbol.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A picture of a '''convex lens'''. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The symbol used in [[diagram]]s to represent a '''convex lens''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Convex Lenses=== | ||
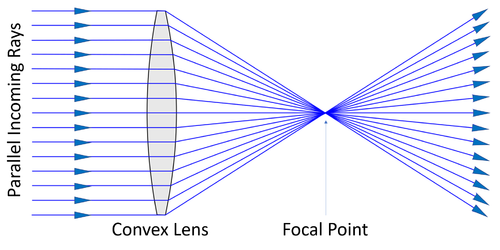
| + | : A '''convex lens''' causes [[parallel]] [[Light Ray|rays]] of [[light]] to [[converge]], so it can also be called a [[Converging Lens|converging lens]]. | ||
| + | : A '''convex''' [[lens]] is used to [[focus]] [[light]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLensFocalPoint.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A '''convex lens''' [[focus|focuses]] [[parallel]] [[Light Ray|rays]] to a [[Focal Point|focal point]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4 Higher== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | A '''convex''' [[lens]] is a shaped piece of [[glass]] that is thickest at the centre and thinnest at the edges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLens.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLensSymbol.png|center|100px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A picture of a '''convex lens'''. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The symbol used in [[diagram]]s to represent a '''convex lens''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Convex Lenses=== | ||
| + | : A '''convex lens''' causes [[parallel]] [[Light Ray|rays]] of [[light]] to [[converge]], so it can also be called a [[Converging Lens|converging lens]]. | ||
| + | : A '''convex''' [[lens]] is used to [[focus]] [[light]]. | ||
| + | : Projecting an [[image]] onto a [[screen]] using a '''convex [[lens]]''' creates a [[Real Image|real image]]. Looking through a '''convex [[lens]]''' the [[image]] seen is a [[Virtual Image|virtual image]]. | ||
| + | : When the [[Object Distance|object distance]] is greater than the [[Focal Length|focal length]] of a '''convex [[lens]]''' the [[image]] produced is [[diminished]] and [[inverted]] (upside down and back to front). | ||
| + | : When the [[Object Distance|object distance]] is less than the [[Focal Length|focal length]] of a '''convex [[lens]]''' the [[image]] produced is [[magnified]] and the right way up. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Finding the Focal Length=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexLensFocalPoint.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A '''convex lens''' [[focus|focuses]] [[parallel]] [[Light Ray|rays]] to a [[Focal Point|focal point]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | : The [[Focal Length|focal length]] of a '''convex lens''' is the distance between the [[Focal Point|focal point]] and the centre of the [[lens]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:FocalLength.png|center|500px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
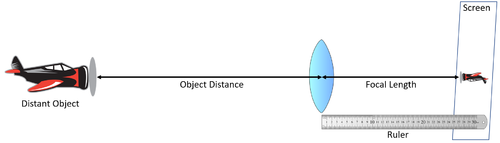
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing how to find the [[Focal Length|focal length]] of a '''convex [[lens]]'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | To find the [[Focal Length]] of a '''convex [[lens]]''': | ||
| + | *[[Focus]] the [[image]] of a "distant object" onto a [[screen]]. | ||
| + | *[[Measure]] the [[distance]] between the [[lens]] and the [[screen]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Image Distance|image distance]] (the distance between the [[focus]]sed [[image]] and the [[lens]]) is the same as the [[Focal Length|focal length]] for a "distant object". | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the [[Object Distance|object distance]] (the distance between an [[object]] and a [[lens]]) is too small, then the [[Image Distance|image distance]] is not the same as the [[Focal Length|focal length]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ray Diagrams=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
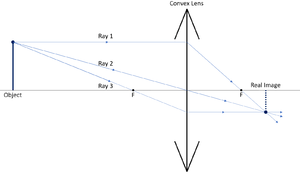
| + | |[[File:ConvexRayDiagram1.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
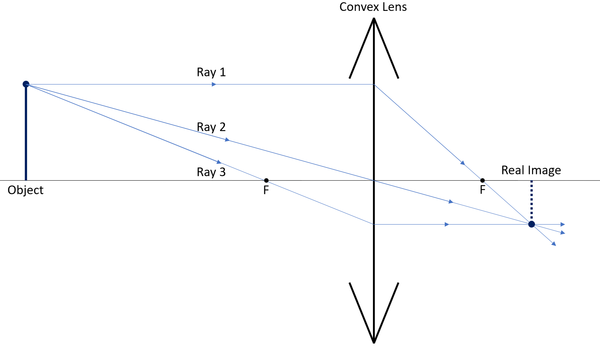
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |A [[Ray Diagram|ray diagram]] for a '''convex [[lens]]'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In this [[diagram]]: | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Ray 1" is shown crossing the [[Focal Point|focal point]] of the [[lens]] after being [[refract]]ed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the [[lens]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Ray 3" is shown crossing the [[Focal Point|focal point]] before the [[lens]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[diagram]] shows that a [[diminish]]ed [[Real Image|real image]] is produced when the [[Object Distance|object distance]] is greater than the [[Focal Length|focal length]] of the '''convex [[lens]]'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
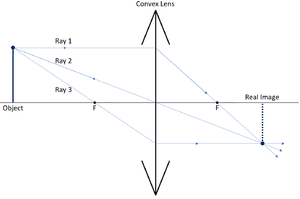
| + | |[[File:ConvexRayDiagram1.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ConvexRayDiagram2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" colspan = "2" |Comparing these two [[diagram]]s shows that the [[image]] size increases as the [[Object Distance|object distance]] approaches the [[Focal Length|focal length]] of the [[lens]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Magnification=== | ||
| + | For further details, see [[magnification]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The equation for the [[magnification]] of a '''convex [[lens]]''' is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | Magnification = (Image Length)/(Object Length) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>Magnification = \frac{L_i}{L_o}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{L_i}</math> = Length of the [[image]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>{L_o}</math> = Length of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Convex lenses, page 208, 211, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Convex lenses, pages 203-4, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Convex lenses, pages 266, 267, 270-272, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac71 ''Convex lenses, pages 82-84, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Convex lenses; magnifying glasses, pages 205-6, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Convex lenses; ray diagrams, pages 204-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Convex lenses; refraction of light, page 203, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Converging lenses, page 118, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Converging lenses, pages 41, 42, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Converging lenses, pages 70, 71, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Converging lenses; images, page 124, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Converging lenses; ray diagrams, pages 122, 123, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:39, 19 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A convex lens is a shaped piece of glass that is thickest at the centre and thinnest at the edges.
| A picture of a convex lens. | The symbol used in diagrams to represent a convex lens |
About Convex Lenses
- A convex lens causes parallel rays of light to converge, so it can also be called a converging lens.
- A convex lens is used to focus light.
| A convex lens focuses parallel rays to a focal point. |
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
A convex lens is a shaped piece of glass that is thickest at the centre and thinnest at the edges.
| A picture of a convex lens. | The symbol used in diagrams to represent a convex lens |
About Convex Lenses
- A convex lens causes parallel rays of light to converge, so it can also be called a converging lens.
- A convex lens is used to focus light.
- Projecting an image onto a screen using a convex lens creates a real image. Looking through a convex lens the image seen is a virtual image.
- When the object distance is greater than the focal length of a convex lens the image produced is diminished and inverted (upside down and back to front).
- When the object distance is less than the focal length of a convex lens the image produced is magnified and the right way up.
Finding the Focal Length
| A convex lens focuses parallel rays to a focal point. |
- The focal length of a convex lens is the distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens.
| A diagram showing how to find the focal length of a convex lens. |
To find the Focal Length of a convex lens:
- Focus the image of a "distant object" onto a screen.
- Measure the distance between the lens and the screen.
The image distance (the distance between the focussed image and the lens) is the same as the focal length for a "distant object".
If the object distance (the distance between an object and a lens) is too small, then the image distance is not the same as the focal length.
Ray Diagrams
| A ray diagram for a convex lens.
In this diagram: "Ray 1" is shown crossing the focal point of the lens after being refracted. "Ray 2" is shown passing through the centre of the lens. "Ray 3" is shown crossing the focal point before the lens. The diagram shows that a diminished real image is produced when the object distance is greater than the focal length of the convex lens. |
| Comparing these two diagrams shows that the image size increases as the object distance approaches the focal length of the lens. | |
Magnification
For further details, see magnification.
The equation for the magnification of a convex lens is:
Magnification = (Image Length)/(Object Length)
\(Magnification = \frac{L_i}{L_o}\)
Where
\({L_i}\) = Length of the image.
\({L_o}\) = Length of the object.
References
AQA
- Convex lenses, page 208, 211, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Convex lenses, pages 203-4, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Convex lenses, pages 266, 267, 270-272, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Convex lenses, pages 82-84, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Convex lenses; magnifying glasses, pages 205-6, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Convex lenses; ray diagrams, pages 204-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Convex lenses; refraction of light, page 203, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Converging lenses, page 118, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Converging lenses, pages 41, 42, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Converging lenses, pages 70, 71, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Converging lenses; images, page 124, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Converging lenses; ray diagrams, pages 122, 123, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel