Difference between revisions of "Ammeter"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Ammeters=== | ===About Ammeters=== | ||
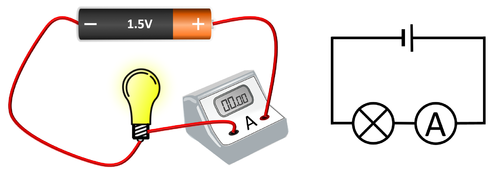
| − | : [[Ammeter]]s are added in [[series]] to a [[circuit]] to find the [[Electrical Current|current]] flowing through the [[circuit]]. | + | : [[Ammeter]]s are added in [[Series Circuit|series]] to a [[circuit]] to find the [[Electrical Current|current]] flowing through the [[circuit]]. |
: An ideal [[ammeter]] has zero [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] because otherwise adding an [[ammeter]] to a [[circuit]] would change the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | : An ideal [[ammeter]] has zero [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] because otherwise adding an [[ammeter]] to a [[circuit]] would change the [[Electrical Current|current]]. | ||
: [[Ammeter]]s can be [[Analogue Ammeter|analogue]] with a needle pointing to numbers on a dial or it can be [[Digital Ammeter|digital]] with a number display. | : [[Ammeter]]s can be [[Analogue Ammeter|analogue]] with a needle pointing to numbers on a dial or it can be [[Digital Ammeter|digital]] with a number display. | ||
Revision as of 12:28, 25 February 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning

A picture showing an analogue ammeter.
An ammeter is a measuring device used to measure electrical current.
About Ammeters
- Ammeters are added in series to a circuit to find the current flowing through the circuit.
- An ideal ammeter has zero resistance because otherwise adding an ammeter to a circuit would change the current.
- Ammeters can be analogue with a needle pointing to numbers on a dial or it can be digital with a number display.
| An ammeter placed in series with a bulb. |