Difference between revisions of "PH Indicator"
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
|[[File:pHIndicators.png|center|600px]] | |[[File:pHIndicators.png|center|600px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Indicators (of pH), page 289, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Indicators (of pH), page 369, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Indicators, page 126, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Indicators, page 52, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Indicators, pages 124, 125, 237, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09996 ''Indicators, pages 128, 134, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Indicators, pages 146, 147, 149, 150, 315, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 01:30, 7 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A pH Indicator is a dye which changes colour depending on the pH of its environment.
About pH Indicators
- The colour of a pH indicator can be used to tell the pH of a solution.
- Different indicators will have a different range of colours for different pH values.
- A good pH indicator can be added to solution without affecting the pH of the solution. If a pH indicator changed the pH of a solution it could not give an accurate reading.
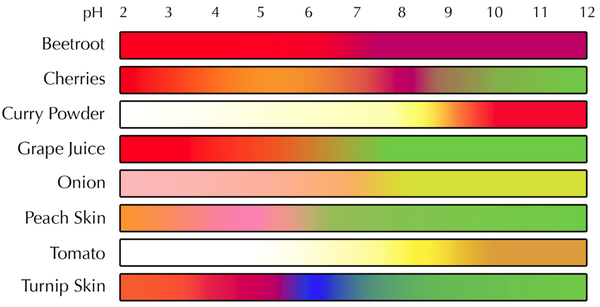
Some pH indicators you should know:
- Litmus Paper
- Red Cabbage Indicator
- Universal Indicator
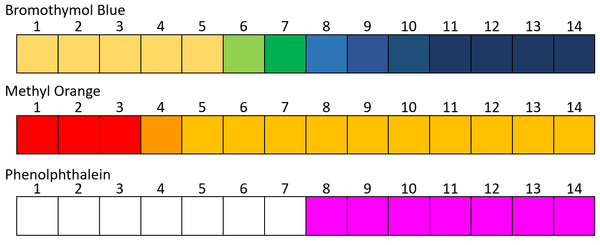
- Phenolphthalein
- Methyl Orange
- Bromothymol Blue
Examples
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A pH indicator is a dye which changes colour depending on the concentration of H+ or OH- ions in solution.
About pH Indicators
- pH indicators are used to determine the pH of a solution.
- Different pH indicators have a different range of effectiveness. Some only have two colours and change between them at a very specific pH. Others can have many different colours over a range of pH values.
References
AQA
- Indicators (of pH), page 289, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Indicators (of pH), page 369, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Indicators, page 126, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Indicators, page 52, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Indicators, pages 124, 125, 237, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Indicators, pages 128, 134, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Indicators, pages 146, 147, 149, 150, 315, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA