Difference between revisions of "Static Electricity"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: A [[material]] that gains [[electron]]s becomes [[Negative Charge|negatively charged]]. | : A [[material]] that gains [[electron]]s becomes [[Negative Charge|negatively charged]]. | ||
: A [[material]] which loses [[electron]]s becomes [[Positive Charge|positively charged]]. | : A [[material]] which loses [[electron]]s becomes [[Positive Charge|positively charged]]. | ||
| − | : Once a [[material]] has become '''statically charged''' it will [[repel]] anything with the same [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and [[attract]] anything with the opposite [[Electrical Charge|charge]]. This happens due to the [[Electrostatic Force]]. | + | : Once a [[material]] has become '''statically charged''' it will [[repel]] anything with the same [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and [[attract]] anything with the opposite [[Electrical Charge|charge]]. This happens due to the [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]]. |
| + | : [[Lightning]] is caused by a build up of '''static electricity''' in which clouds gain [[electron]]s from the ground. The [[Electrical Charge|charge]] builds up until the [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]] is so large that the [[electron]]s are able to jump to the ground as a bolt of [[lightning]]. | ||
| + | |||
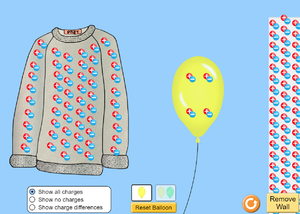
| + | To learn more about [[Static Electricity]] click on each of the picture below for a PHET simulation. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:PhetStatic.png|centre|300px|link=https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/balloons-and-static-electricity/latest/balloons-and-static-electricity_en.html]] | ||
| + | |[[File:PhetTravoltage.png|centre|300px|link=https://phet.colorado.edu/sims/html/john-travoltage/latest/john-travoltage_en.html]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Static Electricity]] is an imbalance of [[Electrical Charge|charges]] that causes a [[force]] which can [[attract]] or [[repel]] other [[Object|objects]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Static Electricity=== | ||
| + | : '''Static Electricity''' can be caused by rubbing two [[Electrical Insulator|insulators]] together. For certain [[material]]s [[electron]]s can be transferred from one [[material]] to the other by [[friction]]. | ||
| + | : A [[material]] that gains [[electron]]s becomes [[Negative Charge|negatively charged]]. | ||
| + | : A [[material]] which loses [[electron]]s becomes [[Positive Charge|positively charged]]. | ||
| + | : Once a [[material]] has become '''statically charged''' it will [[repel]] anything with the same [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and [[attract]] anything with the opposite [[Electrical Charge|charge]]. This happens due to the [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]]. | ||
: [[Lightning]] is caused by a build up of '''static electricity''' in which clouds gain [[electron]]s from the ground. The [[Electrical Charge|charge]] builds up until the [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]] is so large that the [[electron]]s are able to jump to the ground as a bolt of [[lightning]]. | : [[Lightning]] is caused by a build up of '''static electricity''' in which clouds gain [[electron]]s from the ground. The [[Electrical Charge|charge]] builds up until the [[Electrostatic Force|electrostatic force]] is so large that the [[electron]]s are able to jump to the ground as a bolt of [[lightning]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:17, 3 March 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Static Electricity is an imbalance of charges that causes a force which can attract or repel other objects.
About Static Electricity
- Static Electricity can be caused by rubbing two insulators together. For certain materials electrons can be transferred from one material to the other by friction.
- A material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged.
- A material which loses electrons becomes positively charged.
- Once a material has become statically charged it will repel anything with the same charge and attract anything with the opposite charge. This happens due to the electrostatic force.
- Lightning is caused by a build up of static electricity in which clouds gain electrons from the ground. The charge builds up until the electrostatic force is so large that the electrons are able to jump to the ground as a bolt of lightning.
To learn more about Static Electricity click on each of the picture below for a PHET simulation.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Static Electricity is an imbalance of charges that causes a force which can attract or repel other objects.
About Static Electricity
- Static Electricity can be caused by rubbing two insulators together. For certain materials electrons can be transferred from one material to the other by friction.
- A material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged.
- A material which loses electrons becomes positively charged.
- Once a material has become statically charged it will repel anything with the same charge and attract anything with the opposite charge. This happens due to the electrostatic force.
- Lightning is caused by a build up of static electricity in which clouds gain electrons from the ground. The charge builds up until the electrostatic force is so large that the electrons are able to jump to the ground as a bolt of lightning.
To learn more about Static Electricity click on each of the picture below for a PHET simulation.