Difference between revisions of "Ethane"
(→About Methane) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: [[Ethane]] can be [[oxidise]]d to [[product|produce]] [[Carbon Dioxide]] and [[Water]]. | : [[Ethane]] can be [[oxidise]]d to [[product|produce]] [[Carbon Dioxide]] and [[Water]]. | ||
: [[Ethane]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | : [[Ethane]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| − | |||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
Revision as of 10:33, 3 April 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
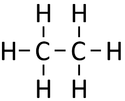
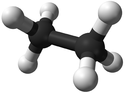
Ethane is a gaseous (at room temperature) hydrocarbon with chemical formula C2H6.
About Ethane
- Ethane is hydrocarbon because it contains only Hydrogen and Carbon atoms.
- Ethane can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Ethane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Ethane is a gaseous (at room temperature) hydrocarbon with chemical formula C2H6.
About Ethane
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | Structural Formula | Structural Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| C2H6 | CH3CH3 |
- Ethane is hydrocarbon because it contains only Hydrogen and Carbon atoms.
- Ethane can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Ethane + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C2H6 + 7O2 -> 4CO2 + 6H2O</chem>