Difference between revisions of "Micro-organism"
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
==Beyond the Curriculum== | ==Beyond the Curriculum== | ||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pHLP5CZMnL4}} | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pHLP5CZMnL4}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Microorganisms, page 122, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Microorganisms, page 269, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Microorganisms, page 330, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Microorganisms, page 46, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Microorganisms, pages 278, 308-309, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Microorganisms; culturing, pages 17, 18, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 16:43, 8 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
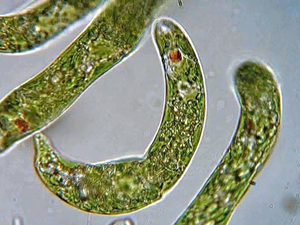
A type of micro-organism called Euglena.
A micro-organism is a living creature so small that it cannot be seen with the eyes.
About Micro-organisms
- There are millions of types of micro-organism.
- Some micro-organisms are good for us. They live in our digestive system and help digest food.
- Some micro-organisms can make us ill. They can cause infections, rashes and sickness.
- We use certain micro-organisms to make foods. Cheese and yoghurt are made by adding micro-organisms to milk. Bread and alcohol are all made by adding micro-organisms to sugary food.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A micro-organism is a unicellular organism.
About Micro-organisms
- There are millions of types of micro-organism.
- Some micro-organisms are good for us. They live in our digestive system and help digest food.
- Some micro-organisms can make us ill. They can cause infections, rashes and sickness.
- Some common micro-organisms you should know:
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A micro-organism is a unicellular organism.
About Micro-organisms
- There are millions of types of micro-organism.
- Some micro-organisms are good for us. They live in our digestive system and help digest food.
- Some micro-organisms can make us ill. They can cause infections, rashes and sickness.
- Some common micro-organisms you should know:
Beyond the Curriculum
References
AQA
- Microorganisms, page 122, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Microorganisms, page 269, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Microorganisms, page 330, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Microorganisms, page 46, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Microorganisms, pages 278, 308-309, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Microorganisms; culturing, pages 17, 18, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA