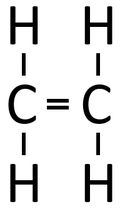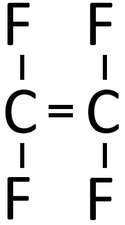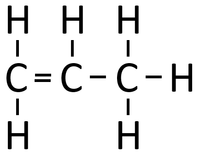Difference between revisions of "Addition Polymerisation"
(→About Addition Polymerisation) |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
===About Addition Polymerisation=== | ===About Addition Polymerisation=== | ||
: In '''addition polymerisation''' the [[monomer]]s join to form a [[polymer]] without any other [[product]]s. | : In '''addition polymerisation''' the [[monomer]]s join to form a [[polymer]] without any other [[product]]s. | ||
| − | : '''Addition polymerisation''' happens between [[alkene]] [[monomer]]s. | + | : '''Addition polymerisation''' happens between [[Unsaturated Hydrocarbon|unsaturated]] [[alkene]] [[monomer]]s. |
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 19 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
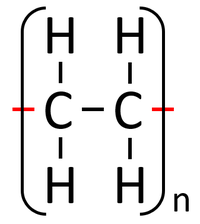
Addition polymerisation is a reaction in which the double bonds within monomers breaks to join the them together into a polymer.
About Addition Polymerisation
- In addition polymerisation the monomers join to form a polymer without any other products.
- Addition polymerisation happens between unsaturated alkene monomers.
Examples
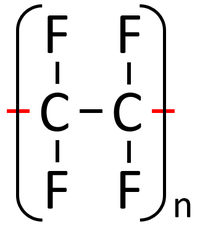
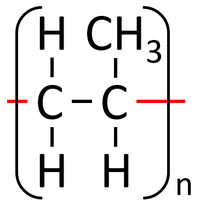
| Polythene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of Ethene monomers. | PolyTetraFluoroEthene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of TetraFluoroEthene monomers. | PolyPropene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of Propene monomers. |