Polymer
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A polymer is a long molecule made by reacting together several smaller molecules.
About Polymers
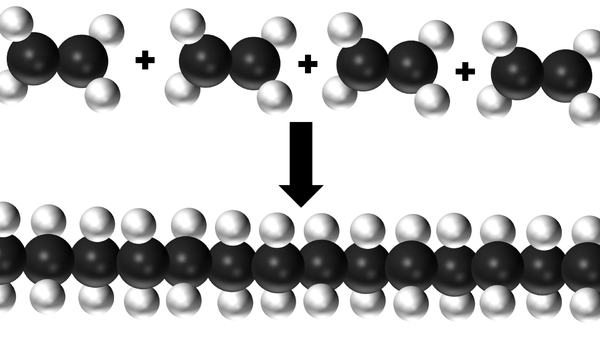
| This diagram shows several Ethene molecules reacting together to make a polythene molecule. |
Different polymers can have different properties but generally polymers are:
- Easily molded into shape.
- Solid at room temperature.
- Plastic in behaviour.
- An Electrical Insulator.
| Polymer | Properties | Application |
| Polythene | Plastic, Strong, Ductile | Shopping bags |
| PVC | Plastic, Electrical Insulator, Strong | Covering of electrical wires. |
| Nylon | Plastic, Strong, Flexible, Ductile. | Clothing |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
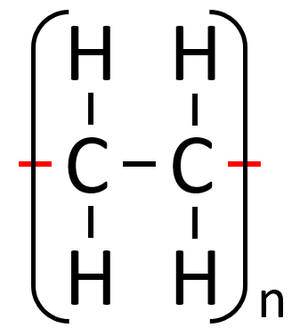
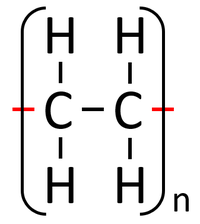
A polymer is represented by showing the part that is repeated over and over. The 'n' represents the fact that it is repeated many times.
A polymer is a large molecule made of many identical smaller molecules called monomers.
About Polymers
- Polymers are held together by covalent bonds.
- The monomers which make up a polymer are simple covalent molecules.
- Most polymers are made of chains of Carbon atoms since they can from up to 4 covalent bonds with adjacent atoms. However, some can be made from Silicon, which can also form 4 covalent bonds.
Examples
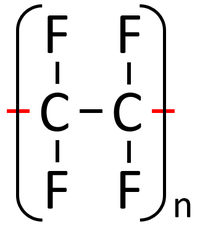
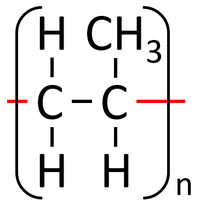
| Polythene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of Ethene monomers. | PolyTetraFluoroEthene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of TetraFluoroEthene monomers. | PolyPropene is a polymer made by reacting thousands of Propene monomers. |
Applications and Properties
| Application | Polymer | Properties |
| Windows | Polymethylmethacrylate | Transparent - Light can pass through.
Flexible - Does not break or shatter when a force is applied. |
| Covering electrical wires | PVC (Polychloroethene) | Plastic - Can be molded into shape.
Electrical Insulator - Prevents electricity leaving the wires. Strong - Is not broken easily when a force is applied. |
| Shopping bags | Polythene | Plastic - Can be molded into shape.
Strong - A very thin bag can hold a large weight. Ductile - Can be stretched into shape. Flexible - Can be bent without breaking. |
| Clothes | Nylon | Plastic - Can be molded into shape.
Strong - A very thin fiber can hold a large weight. Ductile - Can be stretched into fibers. Flexible - Can be bent without breaking. |
Extra Information
References
AQA
- Polymer, page 244, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer, pages 62, 74-5, 226-7, 246-9, 342-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; addition, pages 75, 226-7, 246-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; condensation, pages 75, 226-7, 247-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; cross-linking, page 343, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; natural, pages 226-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; poly(ethene), pages 74-5, 226, 246-7, 254-5, 257, 343, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; poly(propene), pages 75, 246-7, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; polypeptide, page 251, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; polysaccharide, pages 252-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; PVC, pages 74-5, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; thermosetting, page 343, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymer; thermosoftening, page 343, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymerisation, pages 246-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Polymers, page 118, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Polymers, page 158, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers, page 85, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Polymers, pages 148, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers, pages 168-177, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers, pages 33, 80, 83, 84, 96, 97, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Polymers, pages 43, 187, 262-3, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers, pages 87, 236, 237, 244-247, 281-283, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Polymers; addition polymers, pages 187-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers; addition, page 169, 224, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; addition, pages 169, 224, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; condensation polymers, pages 189-91, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers; condensation, pages 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; condensation, pages 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; forces between chains, page 225, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; forces between chains, page 225, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; natural, pages 172-175, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; natural, pages 172-175, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; naturally occurring, pages 193-4, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Polymers; properties, pages 224-225, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Polymers; thermosoftening and thermosetting, page 264, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Polymers, page 86, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Polymers, pages 12, 52, 124, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Polymers, pages 23, 99-101, 106, 107, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Polymers, pages 43, 184, 203, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Polymers, pages 61, 288-295, 313, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Polymers; disposal of, page 101, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Polymers; naturally-occurring, page 185, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Polymers; problems with, pages 190-191, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Polymers; properties and uses, pages 186-187, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Polymers; synthetic, page 185, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
OCR
- Polymers (biological), pages 15, 23, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Polymers, page 29, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers, page 95, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Polymers, pages 23, 86, 87, 90, 91, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Polymers, pages 64-65, 242-247, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; addition, pages 242-243, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; biological, pages 14, 20, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Polymers; biological, pages 64, 65, 244-245, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; condensation, pages 246-247, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; crude oil as raw material, page 241, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; properties, pages 221, 224, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Polymers; recycling, page 227, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR