Simple Covalent Molecule
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Simple covalent molecules are small molecules in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds.
About Simple Covalent Molecules
- Simple covalent molecules are simple in that they have only a small number of atoms.
- Simple covalent molecules can be elements or compounds.
- The covalent bonds in a simple covalent molecule can be represented with a Dot and Cross Diagram.
Examples
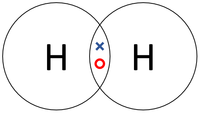
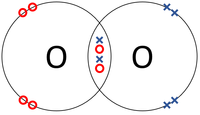
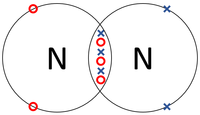
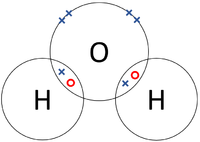
| The two Hydrogen atoms each share one electron with each other. | The two Oxygen atoms each share two of their electrons with one another. | The two Nitrogen atoms each share three of their electrons with one another. |
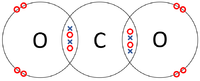
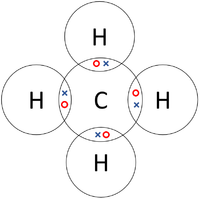
| Each Oxygen shares two of its electrons with the Carbon atom while the Carbon atom shares two electrons with each Oxygen atom. | Each Hydrogen atom shares its only electron with the Oxygen atom and the Oxygen shares one of its electrons with each Hydrogen atom. | Each Hydrogen atom shares its only electron with the Carbon atom and the Carbon atom each of its 4 electrons with the Hydrogen atoms. |
Bulk Properties
- The physical properties of substances made of simple covalent molecules are determined by the the covalent bonds within molecules and the intermolecular bonds between molecules.
- The boiling point and melting point of a simple covalent' substance are determined by the strength of intermolecular bonds. The stronger the intermolecular bonds the higher the boiling point and melting point.
- Substances made of simple covalent molecules are usually poor electrical conductors because charged particles such as electrons or ions are not free to move from one place to another.
- Substances made of simple covalent molecules are usually poor thermal conductors because electrons are not free to move around the material.