Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gas pressure is the pressure on an object caused by a gas.
About Gas Pressure
- Pressure in gases is caused by particles colliding with the object or walls of the container.
- Each time a particle in the gas hits an object or the walls it provides a force.
- The more particles that hit the object or walls, the bigger the overall force it will experience.
- The faster the particles hit the object or walls, the bigger the force that each particle collides with.
|
|
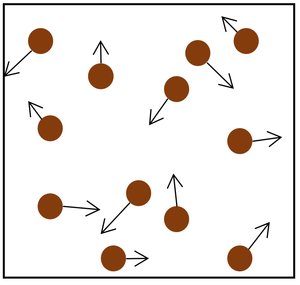
| The particle model of a gas showing the particles as red balls and their speed and direction shown by the arrows. The longer the arrows the faster they are moving.
|
- The gas pressure can be increased in two ways:
|
|
|
| Increasing the temperature of the gas which makes the particles move faster. This causes the particles to hit the walls of the container more often and with a greater force.
|
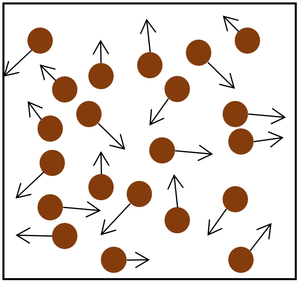
Increasing the number of particles in the container.
|
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gas pressure is the pressure on an object caused by a gas.
About Gas Pressure
- Pressure in gases is caused by particles colliding with the object or walls of the container.
- The pressure from a gas always acts at right angles to the surface.
- Each time a particle in the gas hits an object or the walls it changes momentum which causes a force to be applied to the surface.
- The more particles that hit the surface, the bigger the overall force it will experience.
- The faster the particles hit the object or walls, the bigger the force that each particle collides with.
- The frequency and speed with which the particles collide with the surface determines the pressure on that surface.
|
|
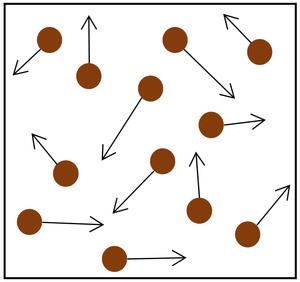
| The particle model of a gas showing the particles as red balls and their speed and direction shown by the arrows. The longer the arrows the faster they are moving.
|
- The gas pressure can be increased in three ways:
|
|
|
| Increasing the temperature of the gas which makes the particles move faster. This causes the particles to hit the walls of the container more often and with a greater force.
|
Increasing the number of particles in the container.
|