Key Stage 3
Meaning
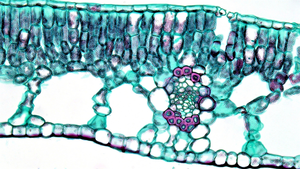
The two guard cells can be seen at the leaf.
A guard cell is a specialised cell in a plant leaf which contains can change shape to allow or stop gases from getting into the leaf.
Adaptations of the Guard Cell
- Guard cells can change shape to open and close a hole called a stoma.
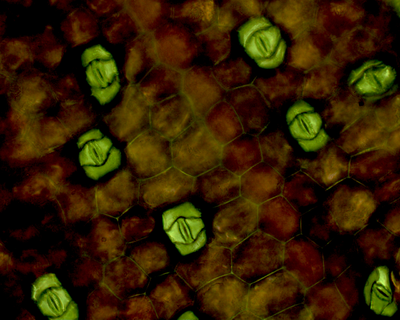
| The under side of a leaf showing guard cells and stomata. |
About Guard Cells
- Guard cells are shaped with a gap between them called a stoma.
- There are more guard cells found on the bottom of the leaf.
- Photosynthesis needs water, so guard cells are there to make sure the leaves don't use up too much water and die of dehydration.
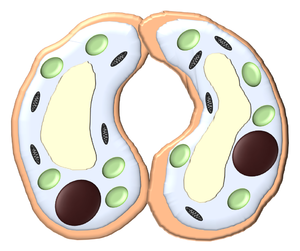
- Guard cells fill with water to become turgid, making the stomata larger. This allows carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis.
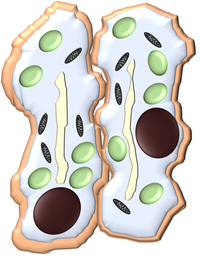
- When the leaf gets dehydrated the guard cells become flaccid making the stomata smaller. This stops carbon dioxide from getting into the leaf and prevents photosynthesis
| Turgid guard cells are full of water and have a hole called a stoma between them to allow air in and out. | Flaccid guard cells are dehydrated and the stoma is blocked stopping air form getting in or out of the leaf. |