Difference between revisions of "Force Pair"
(→Examples) |
(→Examples) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:ForcePairGroundBall.png|center| | + | |[[File:ForcePairGroundBall.png|center|300px]] |
| − | |[[File:ForcePairRocket.png|center| | + | |[[File:ForcePairRocket.png|center|300px]] |
|- | |- | ||
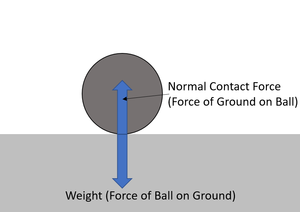
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows the [[weight]] as the "[[Action Force]]" and the [[Normal Contact Force|normal contact force]] as the "[[Reaction Force]]". | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows the [[weight]] as the "[[Action Force]]" and the [[Normal Contact Force|normal contact force]] as the "[[Reaction Force]]". | ||
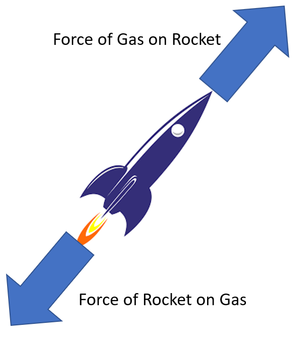
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows a rocket with a '''force pair''' where each [[force]] is equal in [[magnitude]] but opposite in direction. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows a rocket with a '''force pair''' where each [[force]] is equal in [[magnitude]] but opposite in direction. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 14:01, 7 February 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
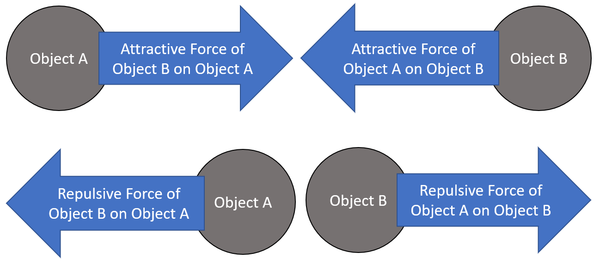
A force pair is the two forces that occur when two objects interact.
About Force Pairs
- The two forces in a force pair may be referred to as an action force and a reaction force.
- When an object "A" exerts a force (action force) on object "B" then object "B" will exert a force (reaction force) on object "A". These are a force pair which will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to one another.
Examples
| This diagram shows a force pair. It does not matter which is labelled "Action Force" and which is labelled "Reaction Force" |
| This diagram shows the weight as the "Action Force" and the normal contact force as the "Reaction Force". | This diagram shows a rocket with a force pair where each force is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. |