Difference between revisions of "Guard Cell"
(→About Guard Cells) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===About Guard Cells=== | ===About Guard Cells=== | ||
: '''Guard cells''' are shaped with a gap between them called a [[stoma]]. | : '''Guard cells''' are shaped with a gap between them called a [[stoma]]. | ||
| − | : There are more '''guard cells''' found on the bottom of the [[leaf]]. | + | : There are more '''guard cells''' found on the bottom of the [[leaf]] than the top. |
: [[Photosynthesis]] needs water, so '''guard cells''' are there to make sure the [[leaf|leaves]] don't use up too much [[water]] and die of [[Dehydrate|dehydration]]. | : [[Photosynthesis]] needs water, so '''guard cells''' are there to make sure the [[leaf|leaves]] don't use up too much [[water]] and die of [[Dehydrate|dehydration]]. | ||
: '''Guard cells''' fill with water to become [[turgid]], making the [[stoma|stomata]] larger. This allows [[Carbon Dioxide|carbon dioxide]] into the [[leaf]] for [[photosynthesis]]. | : '''Guard cells''' fill with water to become [[turgid]], making the [[stoma|stomata]] larger. This allows [[Carbon Dioxide|carbon dioxide]] into the [[leaf]] for [[photosynthesis]]. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
A '''guard cell''' is a [[Specialised Cell|specialised cell]] in a [[plant]] [[leaf]] which can change shape to open or close a hold in the [[leaf]] called a [[stoma]] allowing or preventing [[gas]] exchange. | A '''guard cell''' is a [[Specialised Cell|specialised cell]] in a [[plant]] [[leaf]] which can change shape to open or close a hold in the [[leaf]] called a [[stoma]] allowing or preventing [[gas]] exchange. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Adaptations of the Guard Cell=== | ||
| + | : '''Guard cells''' can change shape to open and close a hole called a [[stoma]]. | ||
===About Guard Cells=== | ===About Guard Cells=== | ||
: '''Guard Cells''' are essential to control the rate of [[photosynthesis]] and [[transpiration]]. | : '''Guard Cells''' are essential to control the rate of [[photosynthesis]] and [[transpiration]]. | ||
: When '''guard cells''' become '''flaccid''', due to [[dehydration]], the [[stomata]] close and [[Water Vapour|water vapour]] can no longer escape the [[leaf]]. This stops [[transpiration]], preventing further [[water]] loss. The closed [[stomata]] also prevent [[Carbon Dioxide]] from entering the [[leaf]], stopping [[photosynthesis]] and conserving [[water]] (which is needed for [[photosynthesis]]. | : When '''guard cells''' become '''flaccid''', due to [[dehydration]], the [[stomata]] close and [[Water Vapour|water vapour]] can no longer escape the [[leaf]]. This stops [[transpiration]], preventing further [[water]] loss. The closed [[stomata]] also prevent [[Carbon Dioxide]] from entering the [[leaf]], stopping [[photosynthesis]] and conserving [[water]] (which is needed for [[photosynthesis]]. | ||
| + | : There are more '''guard cells''' found on the bottom of the [[leaf]] than the top. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:GuardCellClipart.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:GuardCellFlaccidClipart.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
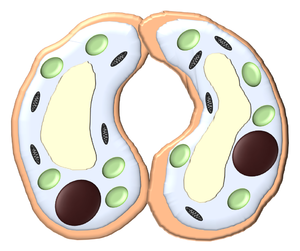
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |[[Turgid]] '''guard cells''' are full of [[water]] and have a hole called a [[stoma]] between them to allow air in and out. | ||
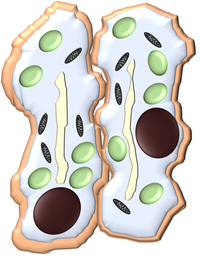
| + | | style="height:20px; width:250px; text-align:center;" |[[Flaccid]] '''guard cells''' are [[dehydrated]] and the [[stoma]] is blocked stopping air form getting in or out of the [[leaf]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:52, 6 June 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
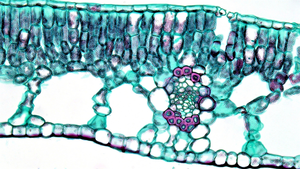
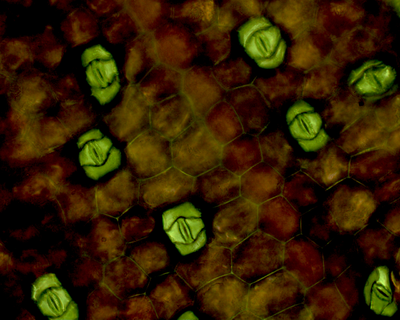
The two guard cells can be seen at the leaf.
A guard cell is a specialised cell in a plant leaf which can change shape to allow or stop gases from getting into the leaf.
Adaptations of the Guard Cell
- Guard cells can change shape to open and close a hole called a stoma.
| The under side of a leaf showing guard cells and stomata. |
About Guard Cells
- Guard cells are shaped with a gap between them called a stoma.
- There are more guard cells found on the bottom of the leaf than the top.
- Photosynthesis needs water, so guard cells are there to make sure the leaves don't use up too much water and die of dehydration.
- Guard cells fill with water to become turgid, making the stomata larger. This allows carbon dioxide into the leaf for photosynthesis.
- When the leaf gets dehydrated the guard cells become flaccid making the stomata smaller. This stops carbon dioxide from getting into the leaf and prevents photosynthesis
| Turgid guard cells are full of water and have a hole called a stoma between them to allow air in and out. | Flaccid guard cells are dehydrated and the stoma is blocked stopping air form getting in or out of the leaf. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A guard cell is a specialised cell in a plant leaf which can change shape to open or close a hold in the leaf called a stoma allowing or preventing gas exchange.
Adaptations of the Guard Cell
- Guard cells can change shape to open and close a hole called a stoma.
About Guard Cells
- Guard Cells are essential to control the rate of photosynthesis and transpiration.
- When guard cells become flaccid, due to dehydration, the stomata close and water vapour can no longer escape the leaf. This stops transpiration, preventing further water loss. The closed stomata also prevent Carbon Dioxide from entering the leaf, stopping photosynthesis and conserving water (which is needed for photosynthesis.
- There are more guard cells found on the bottom of the leaf than the top.
| Turgid guard cells are full of water and have a hole called a stoma between them to allow air in and out. | Flaccid guard cells are dehydrated and the stoma is blocked stopping air form getting in or out of the leaf. |