Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning

A picture of a microphone.
A microphone is an electrical device that turns the vibration of a sound into an electrical signal.
About Microphones
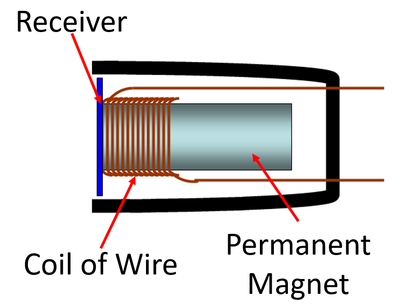
- Sound transfers information which a microphone converts into an electrical signal.
- Microphones use a coil of wire and a permanent magnet to turn a vibration into an electrical signal.
- When the receiver vibrates the coil of wire moves around the permanent magnet to make a current in the coil of wire.
| A diagram of a microphone. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning

A picture of a microphone.
A microphone is an electrical device that turns the vibration of a sound into an electrical signal using the generator effect.
About Microphones
- Sound transfers information which a microphone converts into an electrical signal.
- Microphones use a coil of wire and a permanent magnet to induce a current in the coil when receiver vibrates.
- When the receiver vibrates the coil of wire moves around the permanent magnet to make a current in the coil of wire.
| A diagram of a microphone. |
References
AQA
- Microphone, moving-coil, pages 195, 262, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Microphones, page 225, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Microphones, page 235, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Microphones, page 307, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Microphones, page 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA