Difference between revisions of "State of Matter"
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SolidSquash.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" |'''Solids''' cannot be squashed into a smaller size. You can change their shape, but their size stays the same. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Examples of solid [[Material|materials]]: | Examples of solid [[Material|materials]]: | ||
*Brick | *Brick | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
====Liquid==== | ====Liquid==== | ||
| − | Liquids are a '''state of matter''' that: | + | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Liquids are a '''state of matter''' that: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:LiquidPour.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | *Can be poured and will flow. | ||
*Cannot hold their shape | *Cannot hold their shape | ||
*Fit the shape of the container. | *Fit the shape of the container. | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:LiquidSquash.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" |'''Liquids''' cannot be squashed into a smaller size. You can change their shape, but their size stays the same. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
Examples of liquid [[Material|materials]]: | Examples of liquid [[Material|materials]]: | ||
*Water | *Water | ||
| Line 43: | Line 60: | ||
====Gas==== | ====Gas==== | ||
| − | Gases are a '''state of matter''' that: | + | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ Gases are a '''state of matter''' that: | ||
| + | |- | ||
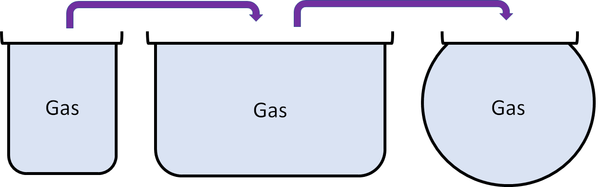
| + | |[[File:GasPour.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" | | ||
*Cannot hold their shape. | *Cannot hold their shape. | ||
*Fit the shape of their container. | *Fit the shape of their container. | ||
*Can be poured and will flow. | *Can be poured and will flow. | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
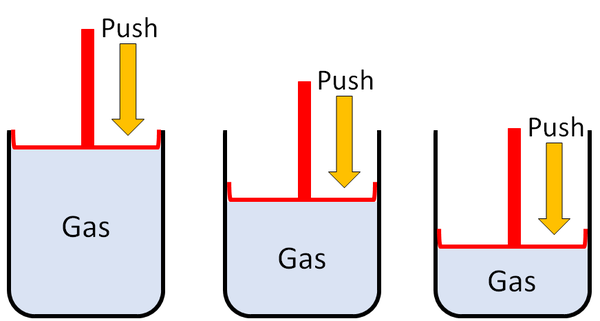
| + | |[[File:GasSquash.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:600px; text-align:left;" |'''Gases''' can be squashed into a smaller size. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
Examples of gas [[Material|materials]]: | Examples of gas [[Material|materials]]: | ||
*Air (A mixture of gases, mostly nitrogen and oxygen) | *Air (A mixture of gases, mostly nitrogen and oxygen) | ||
*Steam | *Steam | ||
Revision as of 19:41, 18 August 2018
Key Stage 2
Meaning
State of matter means whether a material is solid, liquid or gas.
About States of Matter
- Materials can be solid, liquid or gas.
- The state of matter can be changed by heating or cooling the material.
- Heating can turn a solid into a liquid and turn a liquid to a gas.
- Cooling can turn a gas into a liquid and liquid into solid.
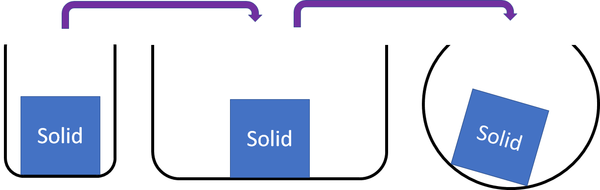
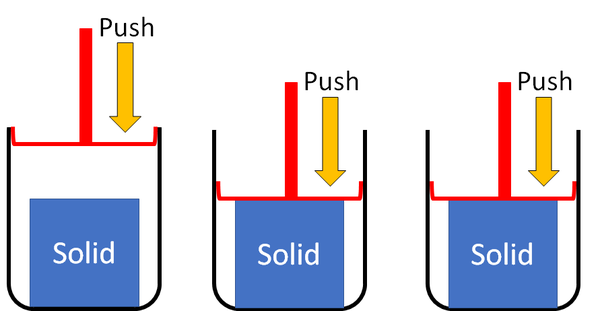
Solid
|
| Solids cannot be squashed into a smaller size. You can change their shape, but their size stays the same. |
Examples of solid materials:
- Brick
- Wood
- Plastic
- Glass
- Ice
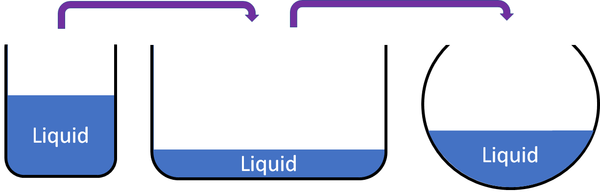
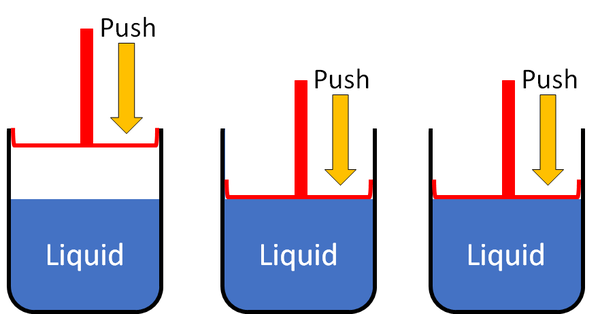
Liquid
|
| Liquids cannot be squashed into a smaller size. You can change their shape, but their size stays the same. |
Examples of liquid materials:
- Water
- Oil
Gas
|
| Gases can be squashed into a smaller size. |
Examples of gas materials:
- Air (A mixture of gases, mostly nitrogen and oxygen)
- Steam