Displacement
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
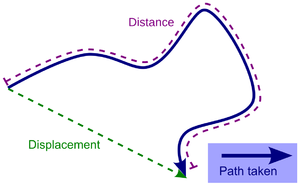
Displacement is a vector quantity describing the straight line distance and direction from a point of origin to a new location.
About Displacement
- Displacement is a vector because it has magnitude and direction.
- The SI Unit for the magnitude of displacement is the metre.
- Displacement is usually described from a point of origin to a new location.
- Displacement is different from it's scalar counterpart 'distance' which describes the length of the journey, while displacement ignores the journey and looks only at the start and end points.
References
AQA
- Displacement, page 147, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Displacement, page 178, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Displacement, page 208, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Displacement, page 60, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Displacement, pages 114, 136, 168-169, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Displacement, pages 118, 148, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Displacement, pages 143, 149, 192, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Displacement, pages 208, 226, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Displacement; calculation from velocity-time graphs, pages 152-3, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Displacement (distance), page 2, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Displacement (distance), page 286, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Displacement (vector), page 145, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Displacement, page 12, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Displacement, page 22, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Displacement (vector), page 157, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Displacement (vector), page 21, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Displacement is the distance moved in a specific direction from a reference point.
About Displacement
- Displacement is a vector quantity, having both magnitude and direction.
- Displacement is different from distance, which is a scalar quantity and only considers the magnitude.
- Displacement is used in kinematics to describe the change in position of an object.
- Displacement is important in understanding motion, as it provides information about the direction of travel.
- Displacement can be positive or negative depending on the chosen reference direction.