GCSE Physics Required Practical: Calculating Densities
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Finding the density of solid objects.
Experiment 1: Cuboid
Method
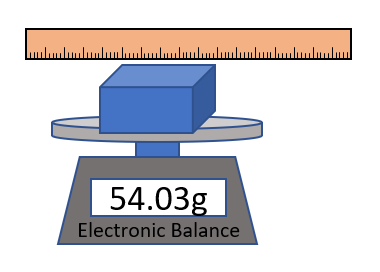
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of a cuboid. |
- Measure the mass of the cuboid using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Measure the length, width and height of the cuboid using a ruler.
- Multiply the length, width and height to calculate the volume.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the cuboid.
Improving Accuracy
- Place the electronic balance on a flat, level surface to get an accurate reading of the mass.
Experiment 1: Irregular Solid
Method
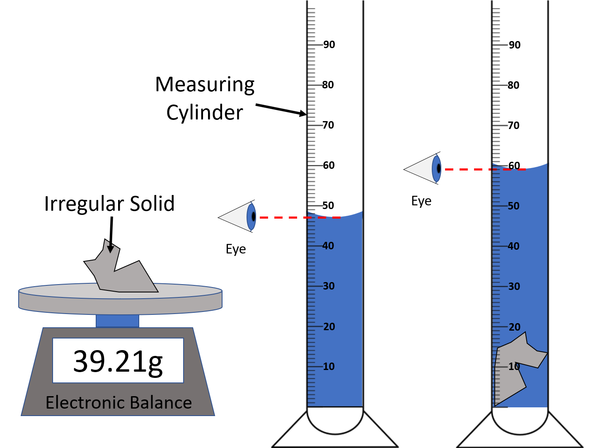
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of an irregular solid. |
- Measure the mass of the object using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Fill a measuring cylinder with enough water to submerse the object.
- Take a reading of the volume of water in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Place the object in the Measuring Cylinder and ensure it is submersed.
- Take a reading of the volume of water + object in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Subtract the volume of water from the volume of water + object to find the volume of the object.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the irregular object.
Improving Accuracy
- Ensure the mass is measured at the start of the experiment so that the mass is measured while the object is dry.
- Place the electronic balance on a flat, level surface to get an accurate reading of the mass.
- Place the measuring cylinder on a flat, level surface and read it from eye level to get an accurate reading of the volume of water.
- Ensure no water is spilled to get an accurate measurement for the volume of the object.
- Ensure the object is fully submerged to get the correct value for the volume of the object.